From hypotonic maintenance fluid to severe hyponatremia: a case report
- PMID: 34099019
- PMCID: PMC8183082
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-021-02889-0
From hypotonic maintenance fluid to severe hyponatremia: a case report
Abstract
Background: The principles for maintenance intravenous fluid prescription in children were developed in the 1950s. These guidelines based on the use of hypotonic solutions have been challenged regularly for they seem to be associated with an increased risk of hospital-acquired hyponatremia.
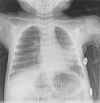
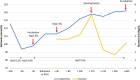
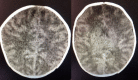
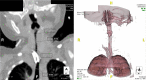
Case presentation: We report the case of a 4-week-old Caucasian child admitted for acute bronchiolitis who received hypotonic maintenance fluids and developed severe hyponatremia (94 mmol/L) with hyponatremic encephalopathy.
Conclusion: This clinical situation can serve as a reminder of the latest recommendations from the American Academy of Pediatrics regarding the use of intravenous fluids that promote the use of isotonic fluids in children.
Keywords: Hyponatremia; Hypotonic fluid; Intensive care; Isotonic fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isotonic versus hypotonic maintenance IV fluids in hospitalized children: a meta-analysis.Pediatrics. 2014 Jan;133(1):105-13. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-2041. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Pediatrics. 2014. PMID: 24379232 Review.
-
Association between maintenance fluid tonicity and hospital-acquired hyponatremia.J Pediatr. 2013 Dec;163(6):1646-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.07.020. Epub 2013 Aug 30. J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23998517 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of isotonic and hypotonic intravenous maintenance fluids: a randomized clinical trial.JAMA Pediatr. 2015 May;169(5):445-51. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.3809. JAMA Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25751673 Clinical Trial.
-
Severe hospital-acquired hyponatremia in acutely ill children receiving moderately hypotonic fluids.Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Feb;37(2):443-448. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-05227-0. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 34398305 Free PMC article.
-
Risks of severe hyponatremia in children receiving hypotonic fluids.Arch Pediatr. 2020 Nov;27(8):474-479. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2020.08.009. Epub 2020 Oct 4. Arch Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33028494 Review.
Cited by
-
Appropriateness of intravenous fluid prescriptions in hospitalised patients: a point prevalence study.Int J Clin Pharm. 2025 Feb;47(1):136-145. doi: 10.1007/s11096-024-01816-9. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Int J Clin Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39527169
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

