Crucial mutation in the exoribonuclease domain of nsp14 of PEDV leads to high genetic instability during viral replication
- PMID: 34099051
- PMCID: PMC8182996
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-021-00598-1
Crucial mutation in the exoribonuclease domain of nsp14 of PEDV leads to high genetic instability during viral replication
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus (CoV) nonstructural protein 14 (nsp14) has exoribonuclease (ExoN) activity, responsible for proofreading and contributing to replication fidelity. It has been reported that CoVs exhibit variable sensitivity to nsp14-ExoN deficiency. Betacoronavirus murine hepatitis virus (MHV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV were viable upon nsp14-ExoN deficiency. While betacoronavirus Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 were non-viable with disabled nsp14-ExoN. In this study, we investigated the nsp14-ExoN deficiency of alphacoronavirus porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) in viral pathogenesis using reverse genetics.
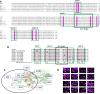
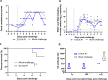
Results: Eight nsp14-ExoN deficient mutants, targeting the predicted active sites and the Zinc finger or mental-coordinating sites, of PEDV were designed. Only one mutant E191A with a mutation in the Mg2+-binding site was rescued using the infectious clone of PEDV PC22A strain (icPC22A). The passage no.1-3 (P1-3) of E191A grew to very low titers in Vero cells. To evaluate the pathogenesis of the E191A, 4 or 5-day-old gnotobiotic pigs were inoculated orally with 100 TCID50/pig of the E191A-P1, icPC22A, or mock. All mock pigs did not shed virus in feces or show clinical signs. All pigs inoculated with icPC22A shed high viral RNA levels, had severe diarrhea, and died by 6 days post-inoculation (dpi). In contrast, only 3 pigs (3/4, 75%) in the E191A-P1 group shed low levels of viral RNA and 2 pigs had moderate diarrhea at acute infection phase. At 22 dpi, each pig was challenged orally with 106 plaque forming unit of virulent icPC22A. All pigs in the mock group developed severe diarrhea and 2 of the 5 pigs died. Pigs in the E191A-P1 group had less severe diarrhea and no pigs died. Sanger sequencing analysis revealed that the viral genome in the fecal sample of one E191A-P1-inoculated pig and the P4 virus passaged in vitro lost the E191A mutation, suggesting the genetic instability of the E191A mutant.
Conclusion: The recombinant PEDV variants carrying mutations at the essential functional sites within nsp14-ExoN were either lethal or genetically unstable. Our finding further confirmed the critical role of nsp14-ExoN in CoV life cycle, suggesting that it may be a target for the design of universal anti-CoV drugs.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Exoribonuclease; Infectious clone; Nsp14; Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus; Reverse genetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Paarlberg PL. Updated Estimated Economic Welfare Impacts of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV). 2014. Available online:http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/174517/2/14-4.Updated%20Estimated%.... Accessed 25 Sept 2015.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

