Anti-Obesity and Lipid Metabolism Effects of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
- PMID: 34099594
- PMCID: PMC9706023
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2102.02015
Anti-Obesity and Lipid Metabolism Effects of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
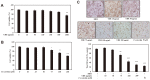
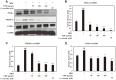
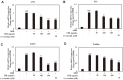
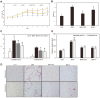
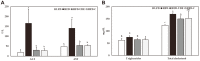
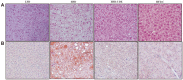
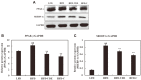
The root bark of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica (Japanese elm) is used in Korea and other East Asian countries as a traditional herbal remedy to treat a variety of inflammatory diseases and ailments such as edema, gastric cancer and mastitis. For this study, we investigated the lipid metabolism and anti-obesity efficacy of ethyl alcohol extract of Ulmus davidiana var. japonica root bark (UDE). First, HPLC was performed to quantify the level of (+)-catechin, the active ingredient of UDE. In the following experiments, cultured 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed murine model were studied for anti-obesity efficacy by testing the lipid metabolism effects of UDE and (+)-catechin. In the test using 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes, treatment with UDE inhibited adipocyte differentiation and significantly reduced the production of adipogenic genes and transcription factors PPARγ, C/EBPα and SREBP-1c. HFD-fed, obese mice were administered with UDE (200 mg/kg per day) and (+)-catechin (30 mg/kg per day) by oral gavage for 4 weeks. Weight gain, epididymal and abdominal adipose tissue mass were significantly reduced, and a change in adipocyte size was observed in the UDE and (+)-catechin treatment groups compared to the untreated control group (***p < 0.001). Significantly lower total cholesterol and triglyceride levels were detected in UDE-treated HFD mice compared to the control, revealing the efficacy of UDE. In addition, it was found that lipid accumulation in hepatocytes was also significantly reduced after administration of UDE. These results suggest that UDE has significant anti-obesity and lipid metabolism effects through inhibition of adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis.
Keywords: (+)-catechin; 3T3-L1; Ulmus davidiana var. japonica; anti-obesity; high-fat diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fermented Platycodon grandiflorum Extract Inhibits Lipid Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.J Med Food. 2016 Nov;19(11):1004-1014. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2016.3805. Epub 2016 Oct 28. J Med Food. 2016. PMID: 27792464
-
Anti-Obesity Effects of the Mixture of Eriobotrya japonica and Nelumbo nucifera in Adipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(4):681-94. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X15500421. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Am J Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26133751
-
Acer tegmentosum Maxim Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3t3-l1 Adipocytes and Attenuates Lipid Accumulation in Obese Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 7;12(12):3753. doi: 10.3390/nu12123753. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33297378 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-obesity effects of resveratrol on the 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2024 Jun;94(3-4):252-263. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000784. Epub 2023 May 30. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2024. PMID: 37248954 Review.
-
Catechin and flavonoid glycosides from the Ulmus genus: Exploring their nutritional pharmacology and therapeutic potential in osteoporosis and inflammatory conditions.Fitoterapia. 2024 Oct;178:106188. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106188. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Fitoterapia. 2024. PMID: 39153558 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Adipogenic and Anti-Obesity Effects of Gongmi Tea and Gongmi So Extract.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023 Mar 31;28(1):21-29. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.1.21. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37066032 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Animal Models for Studying Bone Health in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and Obesity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9399. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179399. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanism of the Anti-Obesity Effects of a Standardized Brassica juncea Extract in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese C57BL/6J Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 15;16(6):846. doi: 10.3390/nu16060846. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542756 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism for Hepatic Glycerolipid Partitioning of n-6/n-3 Fatty Acid Ratio in an Obese Animal Biomodels.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 13;24(2):1576. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021576. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675096 Free PMC article.
-
The Anti-obesity Effects of Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) Seed Red Skin (Testa) Catechins by Regulating Lipoprotein Lipase Expression and Activity.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025 Feb 22;80(1):76. doi: 10.1007/s11130-025-01308-9. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39985678
References
-
- Park JP, Kim JH, Park MK, Yun JW. Potential agents for cancer and obesity treatment with herbal medicines from the green garden. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. 2011;16:1065–1076. doi: 10.1007/s12257-011-0215-3. - DOI

