Oxytocin receptor induces mammary tumorigenesis through prolactin/p-STAT5 pathway
- PMID: 34099636
- PMCID: PMC8184747
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03849-8
Oxytocin receptor induces mammary tumorigenesis through prolactin/p-STAT5 pathway
Abstract
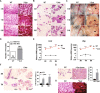
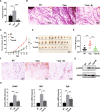
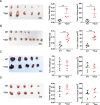
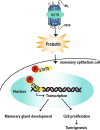
Oxytocin receptor (OXTR) is involved in social behaviors, thermoregulation, and milk ejection, yet little is known about its role in breast cancer. To investigate the role of OXTR in mammary gland development and tumorigenesis, a transgenic mouse model of OXTR overexpression (++Oxtr) was used. Overexpression of OXTR-induced progressive mammary hyperplasia, unexpected milk production, and tumorigenesis in females. OXTR-induced mammary tumors showed ERBB2 upregulation and mixed histological subtypes with predomination of papillary and medullary carcinomas. OXTR overexpression led to an activation of prolactin (PRL)/p-STAT5 pathway and created a microenvironment that promotes mammary-specific tumorigenesis. PRL inhibitor bromocriptine (Br) could mitigate OXTR-driven mammary tumor growth. The study demonstrates Oxtr is an oncogene and a potential drug target for HER2-type breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Andrechek ER, et al. Gene expression profiling of neu-induced mammary tumors from transgenic mice reveals genetic and morphological similarities to ErbB2-expressing human breast cancers. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4920–4926. - PubMed
-
- Pauletti G, Godolphin W, Press MF, Slamon DJ. Detection and quantitation of HER-2/neu gene amplification in human breast cancer archival material using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Oncogene. 1996;13:63–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

