Phase 1 double-blind randomized safety trial of the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 34099646
- PMCID: PMC8185103
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23361-z
Phase 1 double-blind randomized safety trial of the Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
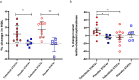
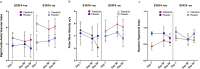
Increased risk of premature cardiovascular disease (CVD) is well recognized in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Aberrant type I-Interferon (IFN)-neutrophil interactions contribute to this enhanced CVD risk. In lupus animal models, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib improves clinical features, immune dysregulation and vascular dysfunction. We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of tofacitinib in SLE subjects (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02535689). In this study, 30 subjects are randomized to tofacitinib (5 mg twice daily) or placebo in 2:1 block. The primary outcome of this study is safety and tolerability of tofacitinib. The secondary outcomes include clinical response and mechanistic studies. The tofacitinib is found to be safe in SLE meeting study's primary endpoint. We also show that tofacitinib improves cardiometabolic and immunologic parameters associated with the premature atherosclerosis in SLE. Tofacitinib improves high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels (p = 0.0006, CI 95%: 4.12, 13.32) and particle number (p = 0.0008, CI 95%: 1.58, 5.33); lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase concentration (p = 0.024, CI 95%: 1.1, -26.5), cholesterol efflux capacity (p = 0.08, CI 95%: -0.01, 0.24), improvements in arterial stiffness and endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation and decrease in type I IFN gene signature, low-density granulocytes and circulating NETs. Some of these improvements are more robust in subjects with STAT4 risk allele.
Conflict of interest statement
The NIH and J.J.O.S. have a patent related to JAK inhibitors and receive royalties. The NIH and J.J.O.S. have had a collaborative agreement and development award (CRADA) with Pfizer that pertains to JAK inhibition and tofacitinib. The NIH and J.J.O.S. have an ongoing CRADA for new JAK inhibitors. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:2110–2121. - PubMed
-
- Weidenbusch M, Kulkarni OP, Anders HJ. The innate immune system in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Sci. 2017;131:625–34.. - PubMed
-
- Manzi S, et al. Age-specific incidence rates of myocardial infarction and angina in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with the Framingham Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997;145:408–415. - PubMed
-
- Giannelou M, Mavragani CP. Cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a comprehensive update. J. Autoimmun. 2017;82:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Sánchez P, Toro-Trujillo E, Muñoz-Velandia OM, García AA, Fernández-Ávila DG. Therapeutic Impact of Statins on the Lipid Profile and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Systematic Review of the Literature and a Meta-analysis. Reumatol Clin. 2019;15:e86–e91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

