The steroid-hormone ecdysone coordinates parallel pupariation neuromotor and morphogenetic subprograms via epidermis-to-neuron Dilp8-Lgr3 signal induction
- PMID: 34099654
- PMCID: PMC8184853
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23218-5
The steroid-hormone ecdysone coordinates parallel pupariation neuromotor and morphogenetic subprograms via epidermis-to-neuron Dilp8-Lgr3 signal induction
Abstract
Innate behaviors consist of a succession of genetically-hardwired motor and physiological subprograms that can be coupled to drastic morphogenetic changes. How these integrative responses are orchestrated is not completely understood. Here, we provide insight into these mechanisms by studying pupariation, a multi-step innate behavior of Drosophila larvae that is critical for survival during metamorphosis. We find that the steroid-hormone ecdysone triggers parallel pupariation neuromotor and morphogenetic subprograms, which include the induction of the relaxin-peptide hormone, Dilp8, in the epidermis. Dilp8 acts on six Lgr3-positive thoracic interneurons to couple both subprograms in time and to instruct neuromotor subprogram switching during behavior. Our work reveals that interorgan feedback gates progression between subunits of an innate behavior and points to an ancestral neuromodulatory function of relaxin signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
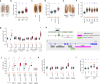
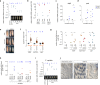


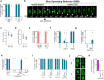
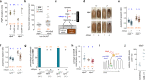
References
-
- Carew TJ. Behavioral Neurobiology: The Cellular Organization of Natural Behavior. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2000.
-
- Cooke S. J., Crossin G. T., Hinch S. G. Pacific salmon migration: completing the cycle. In: Farrell A. P., (ed.), Encyclopedia of Fish Physiology: From Genome to Environment. 3, 1945–1952 (Academic Press, San Diego, Jun 2011).
-
- Turner SE, et al. Birth in free-ranging Macaca fuscata. Int. J. Primatol. 2010;31:15–37. doi: 10.1007/s10764-009-9376-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

