Colchicine inhibits ROS generation in response to glycoprotein VI stimulation
- PMID: 34099810
- PMCID: PMC8184800
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91409-7
Colchicine inhibits ROS generation in response to glycoprotein VI stimulation
Abstract
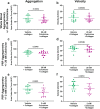
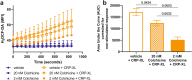
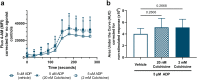
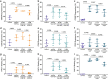
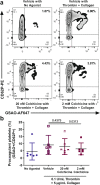
Colchicine inhibits coronary and cerebrovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), and although known to have anti-inflammatory properties, its mechanisms of action are incompletely understood. In this study, we investigated the effects of colchicine on platelet activation with a particular focus on its effects on activation via the collagen glycoprotein (GP)VI receptor, P2Y12 receptor, and procoagulant platelet formation. Therapeutic concentrations of colchicine in vitro (equivalent to plasma levels) significantly decreased platelet aggregation in whole blood and in platelet rich plasma in response to collagen (multiplate aggregometry) and reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation (H2DCF-DA, flow cytometry) in response to GPVI stimulation with collagen related peptide-XL (CRP-XL, GPVI specific agonist). Other platelet activation pathways including P-selectin expression, GPIIb/IIIa conformational change and procoagulant platelet formation (GSAO+/CD62P+) (flow cytometry) were inhibited with higher concentrations of colchicine known to inhibit microtubule depolymerization. Pathway specific mechanisms of action of colchicine on platelets, including modulation of the GPVI receptor pathway at low concentrations, may contribute to its protective role in CAD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Doxepin inhibits GPVI-dependent platelet Ca2+ signaling and collagen-dependent thrombus formation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):C765-C774. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00262.2016. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28404545
-
A Synthetic Triple Helical Collagen Peptide as a New Agonist for Flow Cytometric Measurement of GPVI-Specific Platelet Activation.Thromb Haemost. 2019 Dec;119(12):2005-2013. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1697660. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31634956
-
The collagen receptor glycoprotein VI promotes platelet-mediated aggregation of β-amyloid.Sci Signal. 2020 Aug 4;13(643):eaba9872. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aba9872. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32753479
-
Regulation of platelet activation and thrombus formation by reactive oxygen species.Redox Biol. 2018 Apr;14:126-130. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.08.021. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 28888895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-collagen interaction: is GPVI the central receptor?Blood. 2003 Jul 15;102(2):449-61. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3882. Epub 2003 Mar 20. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12649139 Review.
Cited by
-
Perspective: Collagen induced platelet activation via the GPVI receptor as a primary target of colchicine in cardiovascular disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 19;9:1104744. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1104744. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36741844 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging insights into the role of IL-1 inhibitors and colchicine for inflammation control in type 2 diabetes.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Jun 25;16(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01369-x. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. Retraction in: Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Jan 20;17(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01596-w. PMID: 38918878 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Combination of Colchicine and Ticagrelor Inhibits Carrageenan-Induced Thrombi in Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 17;2022:3087198. doi: 10.1155/2022/3087198. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35082966 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with Platelet Activation-Recent Pharmaceutical Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 18;23(6):3301. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063301. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Mediators of Platelet Activation: Focus on Atherosclerosis and COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 16;22(20):11170. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011170. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

