Axicabtagene ciloleucel in vivo expansion and treatment outcome in aggressive B-cell lymphoma in a real-world setting
- PMID: 34100900
- PMCID: PMC8238487
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003959
Axicabtagene ciloleucel in vivo expansion and treatment outcome in aggressive B-cell lymphoma in a real-world setting
Erratum in
-
Ayuk FA, Berger C, Badbaran A, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel in vivo expansion and treatment outcome in aggressive B-cell lymphoma in a real-world setting. Blood Adv. 2021;5(11):2523-2527.Blood Adv. 2022 Dec 13;6(23):6075. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008370. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 36459166 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
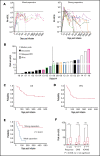
Data on the association between chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell kinetics and patient outcome in the nontrial setting are missing, mainly due to the lack of broadly available CAR-T-cell diagnostic quantification tools. We performed prospective quantification of axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) in 21 patients treated for aggressive B-cell lymphoma at our clinic. Median peak CAR-T-cell count was 16.14 CAR-T cells/µL. Patients with 16.14/μL or higher peak CAR-T cells (strong expanders) had more day-30 objective responses (91% vs 40%, P = .02). In univariate analysis, peak CAR-T cell ≥ 16.14 (P < .001), normal platelet counts at start of lymphodepletion (P < .001), no prior stem cell transplant (P = .04), and peak CAR-T cells as continuous variable (P = .03) were associated with better progression-free survival (PFS). After adjusting for platelet counts and prior stem cell transplantation, peak CAR-T cells below median was still associated with shorter PFS (relative risk, 0.15, 95% confidence interval, 0.04-0.59, P = .007). Low platelet counts also maintained significant impact on PFS. Our data demonstrate association of axi-cel levels and outcome in a nontrial setting and for the first time use a cutoff to segregate weak and strong expanders with respective outcomes.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. ; JULIET Investigators. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45-56. - PubMed

