Isorhapontigenin ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating Kinase Cε/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 34102010
- PMCID: PMC8323036
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2143
Isorhapontigenin ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating Kinase Cε/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Isorhapontigenin (ISO) has been shown to have antioxidant activity. This study aimed to investigate the antioxidant effects of ISO on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and its possible molecular mechanisms.
Methods: Focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (MCAO/R) model and primary cortical neurons were established an oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD / R) injury model. After 24 hr of reperfusion, the neurological deficits of the rats were analyzed and HE staining was performed, and the infarct volume was calculated by TTC staining. In addition, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) in rat brain tissue, the content of 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), and 8-hydroxy2deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) were detected. Neuronal cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Western blot analysis was determined for protein expression.
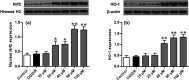
Results: ISO treatment significantly improved neurological scores, reduced infarct volume, necrotic neurons, ROS production, 4-HNE, and 8-OHdG levels. At the same time, ISO significantly increased the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1. The neuroprotective effects of ISO can be eliminated by knocking down Nrf2 and HO-1. In addition, knockdown of the PKCε blocked ISO-induced nuclear Nfr2, HO-1 expression.
Conclusion: ISO protected against oxidative damage induced by brain I/R, and its neuroprotective mechanism may be related to the PKCε/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Keywords: HO-1; Nrf2; PKCε; cerebral ischemia; isorhapontigenin; oxidative stress; reperfusion.
© 2021 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Abiko, Y. , Mizokawa, M. , & Kumagai, Y. J. (2014). Activation of the Kelch‐like ECH‐associated protein 1 (Keap1)/NF‐E2‐related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway through covalent modification of the 2‐Alkenal group of aliphatic electrophiles in Coriandrum sativum L. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(45), 10936‐10944. - PubMed
-
- Carden, D. L. (2015). Pathophysiology of ischaemia‐reperfusion injury. The Journal of Pathology, 190(3), 255–266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

