What gastroenterologists should know about SARS-CoV 2 vaccine: World Endoscopy Organization perspective
- PMID: 34102015
- PMCID: PMC8242672
- DOI: 10.1002/ueg2.12103
What gastroenterologists should know about SARS-CoV 2 vaccine: World Endoscopy Organization perspective
Abstract
Background: The novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) has caused almost 2 million deaths worldwide. Both Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency have recently approved the first COVID-19 vaccines, and a few more are going to be approved soon.
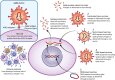
Methods: Several different approaches have been used to stimulate the immune system in mounting a humoral response. As more traditional approaches are under investigation (inactivated virus vaccines, protein subunit vaccines, recombinant virus vaccines), more recent and innovative strategies have been tried (non-replicating viral vector vaccines, RNA based vaccines, DNA based vaccines).
Results: Since vaccinations campaigns started in December 2020 in both the US and Europe, gastroenterologists will be one of the main sources of information regarding SARS-CoV 2 vaccination for patients in their practice, including vulnerable patients such as those with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), patients with chronic liver disease, and GI cancer patients.
Conclusions: Thus, we must ourselves be well educated and updated in order to provide unambiguous counseling to these categories of vulnerable patients. In this commentary, we aim to provide a comprehensive review of both approved COVID-19 vaccines and the ones still under development, and explore potential risks, benefits and prioritization of vaccination.
Keywords: Coronavirus; endoscopy; prevention; public health; vaccine.
© 2021 The Authors. United European Gastroenterology Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. on behalf of United European Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Pneumonia of unknown caused China. https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumoniaof-unkown-cause-chi.... 14 February 2020.
-
- COVID‐19 CORONAVIRUS PANDEMIC . Last updated: January 16, 2021, 13:03 GMT. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/.
-
- Arun TK. Coronavirus: is there an alternative to lockdowns? Economic Times. WHO. 2020. Coronavirus Disease (COVID‐19) Advice for the Public. Geneva, Switzerland; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/advice‐f.... Updated WHO Recommendations for International Traffic in Relation to the COVID‐19 Outbreak. Geneva, Switzerland; 2020 [Feb 29th 2020]. Available from: https://www.who.int/newsroom/articles-detail/updated-who-recommendations...
-
- Canziani LM, Trovati S, Brunetta E, Testa A, De Santis M, Bombardieri E, et al. Humanitas and Gavazzeni/Castelli COVID‐19 Task Forces. Interleukin‐6 receptor blocking with intravenous tocilizumab in COVID‐19 severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective case‐control survival analysis of 128 patients. J Autoimmun. 2020;114:102511. 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102511. Epub 2020 Jul 8. PMID: 32713677; PMCID: PMC7342030 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous