Delayed Antibody and T-Cell Response to BNT162b2 Vaccination in the Elderly, Germany
- PMID: 34102097
- PMCID: PMC8314803
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2708.211145
Delayed Antibody and T-Cell Response to BNT162b2 Vaccination in the Elderly, Germany
Abstract
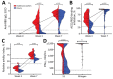
We detected delayed and reduced antibody and T-cell responses after BNT162b2 vaccination in 71 elderly persons (median age 81 years) compared with 123 healthcare workers (median age 34 years) in Germany. These data emphasize that nonpharmaceutical interventions for coronavirus disease remain crucial and that additional immunizations for the elderly might become necessary.
Keywords: B cell; Berlin; COVID-19; Germany; SARS-CoV-2; T cell; antibody; coronavirus disease; immunity; mRNA; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; vaccine; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

