Identification of anti-Parkinson's Disease Lead Compounds from Aspergillus ochraceus Targeting Adenosin Receptors A2A
- PMID: 34102706
- PMCID: PMC8186885
- DOI: 10.1002/open.202100022
Identification of anti-Parkinson's Disease Lead Compounds from Aspergillus ochraceus Targeting Adenosin Receptors A2A
Abstract
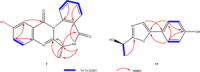
Two novel alkaloids compounds together with fifteen know metabolites were identified from Aspergillus ochraceus. The stereochemistry features of the new molecules were determined via HRESIMS, NMR, ECD, and XRD analyses. Amongst these, compounds two compounds exhibited potential efficacy as anti-Parkinson's disease with the EC50 values of 2.30 and 2.45 μM, respectively. ADMET prediction showed that these compounds owned favorable drug-like characteristics and safe toxicity scores towards CNS drugs. Virtual screening analyses manifested that the compounds exhibited not only robust and reliable interactions to adenosine receptors A2A , but also higher binding selectivity to A2A receptors than to A1 and A3 receptors. Molecular dynamics simulation demonstrated the reliability of molecular docking results and the stability of the complexes obtained with the novel compounds and A2A receptors in natural environments. It is the first time that anti-PD lead compounds have been identified from Aspergillus ochraceus and targeting adenosine A2A receptors.
Keywords: Aspergillus ochraceus; Parkinson's disease; adenosine receptors; alkaloids; drug discovery; virtual screening.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
JNJ-40255293, a novel adenosine A2A/A1 antagonist with efficacy in preclinical models of Parkinson's disease.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Oct 15;5(10):1005-19. doi: 10.1021/cn5001606. Epub 2014 Sep 24. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25203719
-
Discovery of indolylpiperazinylpyrimidines with dual-target profiles at adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors for Parkinson's disease treatment.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 5;13(1):e0188212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188212. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29304113 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Novel and Selective Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists for Treating Parkinson's Disease through Comparative Structure-Based Virtual Screening.J Chem Inf Model. 2017 Jun 26;57(6):1474-1487. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00188. Epub 2017 May 15. J Chem Inf Model. 2017. PMID: 28463561
-
Adenosine A2A-D2 receptor-receptor interactions in putative heteromers in the regulation of the striato-pallidal gaba pathway: possible relevance for parkinson's disease and its treatment.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014;15(7):673-80. doi: 10.2174/1389203715666140901103205. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014. PMID: 25175458 Review.
-
Adenosine A2A receptor antagonists in Parkinson's disease: progress in clinical trials from the newly approved istradefylline to drugs in early development and those already discontinued.CNS Drugs. 2014 May;28(5):455-74. doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0161-7. CNS Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24687255 Review.
Cited by
-
The Secondary Metabolites and Biosynthetic Diversity From Aspergillus ochraceus.Front Chem. 2022 Aug 25;10:938626. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.938626. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36092677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notoamide R: A Prominent Diketopiperazine Fermentation Metabolite amongst Others of Aspergillus ochraceus in the Absence of Ochratoxins.Molecules. 2023 Apr 17;28(8):3518. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083518. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110751 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus ochraceus: Metabolites, Bioactivities, Biosynthesis, and Biotechnological Potential.Molecules. 2022 Oct 10;27(19):6759. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196759. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Prenylated Indole Alkaloids with Neuroprotection on SH-SY5Y Cells against Oxidative Stress Targeting Keap1-Nrf2.Mar Drugs. 2022 Mar 4;20(3):191. doi: 10.3390/md20030191. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35323490 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosinergic Pathway in Parkinson's Disease: Recent Advances and Therapeutic Perspective.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jun;60(6):3054-3070. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03257-3. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36786912 Review.
References
-
- Davie C. A., Br. Med. Bull. 2008, 86, 109–127. - PubMed
-
- Moore T. J., Glenmullen J., Mattison D. R., Jama 2014, 174, 1930–1933. - PubMed
-
- Ko W. K. D., Camus S. M., Li Q., Yang J., McGuire S., Pioli E. Y., Bezard E., Neuropharmacology 2016, 110, 48–58. - PubMed
-
- Delgadillo I., Mycotoxin Res. 1986, 2, 9–17. - PubMed
-
- Tan Y., Yang B., Lin X., Luo X., Pang X., Tang L., Liu Y., Li X., Zhou X., J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 92–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31700298/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31700294/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- M20181008/National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of High-throughput Drug Screening Technology
- S201910512010/Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduates
- S202010512054/Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduates
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

