Identification of anti-Parkinson's Disease Lead Compounds from Aspergillus ochraceus Targeting Adenosin Receptors A2A
- PMID: 34102706
- PMCID: PMC8186885
- DOI: 10.1002/open.202100022
Identification of anti-Parkinson's Disease Lead Compounds from Aspergillus ochraceus Targeting Adenosin Receptors A2A
Abstract
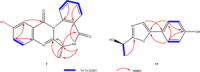
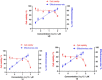
Two novel alkaloids compounds together with fifteen know metabolites were identified from Aspergillus ochraceus. The stereochemistry features of the new molecules were determined via HRESIMS, NMR, ECD, and XRD analyses. Amongst these, compounds two compounds exhibited potential efficacy as anti-Parkinson's disease with the EC50 values of 2.30 and 2.45 μM, respectively. ADMET prediction showed that these compounds owned favorable drug-like characteristics and safe toxicity scores towards CNS drugs. Virtual screening analyses manifested that the compounds exhibited not only robust and reliable interactions to adenosine receptors A2A , but also higher binding selectivity to A2A receptors than to A1 and A3 receptors. Molecular dynamics simulation demonstrated the reliability of molecular docking results and the stability of the complexes obtained with the novel compounds and A2A receptors in natural environments. It is the first time that anti-PD lead compounds have been identified from Aspergillus ochraceus and targeting adenosine A2A receptors.
Keywords: Aspergillus ochraceus; Parkinson's disease; adenosine receptors; alkaloids; drug discovery; virtual screening.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

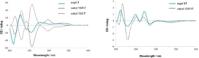




References
-
- Davie C. A., Br. Med. Bull. 2008, 86, 109–127. - PubMed
-
- Moore T. J., Glenmullen J., Mattison D. R., Jama 2014, 174, 1930–1933. - PubMed
-
- Ko W. K. D., Camus S. M., Li Q., Yang J., McGuire S., Pioli E. Y., Bezard E., Neuropharmacology 2016, 110, 48–58. - PubMed
-
- Delgadillo I., Mycotoxin Res. 1986, 2, 9–17. - PubMed
-
- Tan Y., Yang B., Lin X., Luo X., Pang X., Tang L., Liu Y., Li X., Zhou X., J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 92–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31700298/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31700294/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- M20181008/National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of High-throughput Drug Screening Technology
- S201910512010/Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduates
- S202010512054/Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for Undergraduates
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

