Can 18F-FDG PET/CT predict EGFR status in patients with non-small cell lung cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34103313
- PMCID: PMC8190055
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044313
Can 18F-FDG PET/CT predict EGFR status in patients with non-small cell lung cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to explore the diagnostic significance of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/CT for predicting the presence of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Design: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Data sources: The PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane library databases were searched from the earliest available date to December 2020.
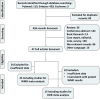
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: The review included primary studies that compared the mean maximum of standard uptake value (SUVmax) between wild-type and mutant EGFR, and evaluated the diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT using SUVmax for prediction of EGFR status in patients with NSCLC.
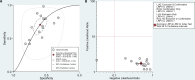
Data extraction and synthesis: The main analysis was to assess the sensitivity and specificity, the positive diagnostic likelihood ratio (DLR+) and DLR-, as well as the diagnostic OR (DOR) of SUVmax in prediction of EGFR mutations. Each data point of the summary receiver operator characteristic (SROC) graph was derived from a separate study. A random effects model was used for statistical analysis of the data, and then diagnostic performance for prediction was further assessed.
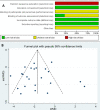
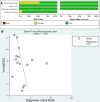
Results: Across 15 studies (3574 patients), the pooled sensitivity for 18F-FDG PET/CT was 0.70 (95% CI 0.60 to 0.79) with a pooled specificity of 0.59 (95% CI 0.52 to 0.66). The overall DLR+ was 1.74 (95% CI 1.49 to 2.03) and DLR- was 0.50 (95% CI 0.38 to 0.65). The pooled DOR was 3.50 (95% CI 2.37 to 5.17). The area under the SROC curve was 0.68 (95% CI 0.64 to 0.72). The likelihood ratio scatter plot based on average sensitivity and specificity was in the lower right quadrant.
Conclusion: Meta-analysis results showed 18F-FDG PET/CT had low pooled sensitivity and specificity. The low DOR and the likelihood ratio scatter plot indicated that 18F-FDG PET/CT should be used with caution when predicting EGFR mutations in patients with NSCLC.
Keywords: genetics; nuclear radiology; respiratory tract tumours.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The diagnostic and predictive efficacy of 18F-FDG PET/CT metabolic parameters for EGFR mutation status in non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2021 Aug;141:109792. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109792. Epub 2021 May 26. Eur J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34062472
-
Predictive value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Nov;11(11):3260-3268. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13664. Epub 2020 Sep 20. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32951338 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Value of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography or Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography for Assessment of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncology. 2021;99(2):96-104. doi: 10.1159/000509988. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Oncology. 2021. PMID: 32980838
-
Role of [¹⁸F]FDG PET in prediction of KRAS and EGFR mutation status in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014 Nov;41(11):2058-65. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2833-4. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24990403
-
Predictive value of multiple metabolic and heterogeneity parameters of 18F-FDG PET/CT for EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer.Ann Nucl Med. 2022 Apr;36(4):393-400. doi: 10.1007/s12149-022-01718-8. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Ann Nucl Med. 2022. PMID: 35084711
Cited by
-
Predictive value of 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics for EGFR mutation status in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 1;14:1281572. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1281572. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38361781 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled EGFR TKI as predictive imaging biomarkers in NSCLC patients - an overview.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 12;12:900450. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.900450. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The predictive value of [18F]FDG PET/CT radiomics combined with clinical features for EGFR mutation status in different clinical staging of lung adenocarcinoma.EJNMMI Res. 2023 Apr 4;13(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13550-023-00977-4. EJNMMI Res. 2023. PMID: 37014500 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer learning-based PET/CT three-dimensional convolutional neural network fusion of image and clinical information for prediction of EGFR mutation in lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Mar 4;24(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01232-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38438844 Free PMC article.
-
Recent and current advances in PET/CT imaging in the field of predicting epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 6;12:879341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.879341. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
