Vitamin D Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in A549 Cells by Downregulating Inflammatory Cytokines
- PMID: 34103463
- PMCID: PMC8202123
- DOI: 10.12659/MSMBR.931481
Vitamin D Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Inflammation in A549 Cells by Downregulating Inflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
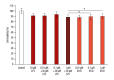
BACKGROUND Studies have shown that lung inflammation affects lung function, with life-threatening results. Vitamin D may play an important role in inhibiting inflammatory cytokines. Vitamin D deficiency is related to several lung problems, including respiratory distress syndrome, alveolar inflammation, epithelial damage, and hypoxia. Few studies have evaluated the benefits of vitamin D in preventing inflammation in alveolar cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS We developed a cell inflammation model induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment. The effects of vitamin D on LPS-induced inflammation in A549 cells were examined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, and the anti-inflammatory mechanism of vitamin D was evaluated using western blot analysis. RESULTS Our results indicated that vitamin D promoted A549 cell survival following LPS-induced inflammation by downregulating nuclear factor nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1ß, IL-6, and IL-12. CONCLUSIONS Our results indicated that vitamin D has the potential to manage lung inflammation, although further studies are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Locci G, Fanos V, Gerosa C, Faa G. Hyaline membrane disease (HMD) : The role of the perinatal pathologist. J Pediatr Neonatal Individ Med. 2014;3(2):1–9.
-
- Ueta M, Hamuro J, Kiyono H, Kinoshita S. Triggering of TLR3 by polyI: C in human corneal epithelial cells to induce inflammatory cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;331(1):285–94. - PubMed
-
- Chow JC, Young DW, Golenbock DT, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 274(16):10689–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

