RIP3 impedes transcription factor EB to suppress autophagic degradation in septic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 34103472
- PMCID: PMC8187512
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03865-8
RIP3 impedes transcription factor EB to suppress autophagic degradation in septic acute kidney injury
Abstract
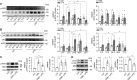
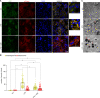
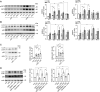
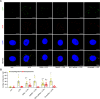
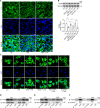
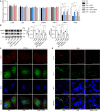
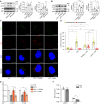
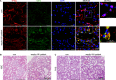
Autophagy is an important renal-protective mechanism in septic acute kidney injury (AKI). Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 (RIP3) has been implicated in the renal tubular injury and renal dysfunction during septic AKI. Here we investigated the role and mechanism of RIP3 on autophagy in septic AKI. We showed an activation of RIP3, accompanied by an accumulation of the autophagosome marker LC3II and the autophagic substrate p62, in the kidneys of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced septic AKI mice and LPS-treated cultured renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTECs). The lysosome inhibitor did not further increase the levels of LCII or p62 in LPS-treated PTECs. Moreover, inhibition of RIP3 attenuated the aberrant accumulation of LC3II and p62 under LPS treatment in vivo and in vitro. By utilizing mCherry-GFP-LC3 autophagy reporter mice in vivo and PTECs overexpression mRFP-GFP-LC3 in vitro, we observed that inhibition of RIP3 restored the formation of autolysosomes and eliminated the accumulated autophagosomes under LPS treatment. These results indicated that RIP3 impaired autophagic degradation, contributing to the accumulation of autophagosomes. Mechanistically, the nuclear translocation of transcription factor EB (TFEB), a master regulator of the lysosome and autophagy pathway, was inhibited in LPS-induced mice and LPS-treated PTECs. Inhibition of RIP3 restored the nuclear translocation of TFEB in vivo and in vitro. Co-immunoprecipitation further showed an interaction of RIP3 and TFEB in LPS-treated PTECs. Also, the expression of LAMP1 and cathepsin B, two potential target genes of TFEB involved in lysosome function, were decreased under LPS treatment in vivo and in vitro, and this decrease was rescued by inhibiting RIP3. Finally, overexpression of TFEB restored the autophagic degradation in LPS-treated PTECs. Together, the present study has identified a pivotal role of RIP3 in suppressing autophagic degradation through impeding the TFEB-lysosome pathway in septic AKI, providing potential therapeutic targets for the prevention and treatment of septic AKI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of LAPTM4B Contributes to the Impairment of the Autophagic Flux via Unopposed Activation of mTORC1 Signaling During Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Circ Res. 2020 Sep 11;127(7):e148-e165. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316388. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32693673
-
Advanced glycation end-products suppress autophagic flux in podocytes by activating mammalian target of rapamycin and inhibiting nuclear translocation of transcription factor EB.J Pathol. 2018 Jun;245(2):235-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5077. Epub 2018 Apr 30. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29570219 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired TFEB-mediated lysosomal biogenesis promotes the development of pancreatitis in mice and is associated with human pancreatitis.Autophagy. 2019 Nov;15(11):1954-1969. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1596486. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30894069 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagic stagnation: a key mechanism in kidney disease progression linked to aging and obesity.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025 Jun;29(6):711-719. doi: 10.1007/s10157-025-02653-4. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40131605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The advances on autophagy the pathogenesis and treatment in septic acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Feb;37(2):183-187. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240904-00748. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40017369 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
CTSB promotes sepsis-induced acute kidney injury through activating mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 13;13:1053754. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1053754. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36713420 Free PMC article.
-
TFEB Dependent Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway: An Emerging Pharmacological Target in Sepsis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 26;12:794298. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.794298. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathological role of damaged organelles in renal tubular epithelial cells in the progression of acute kidney injury.Cell Death Discov. 2022 May 2;8(1):239. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01034-0. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35501332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin Induces Autophagy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Mice via Upregulation of SIRT1.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Aug;59(8):4747-4760. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02875-7. Epub 2022 May 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35606613
-
The Programmed Cell Death of Macrophages, Endothelial Cells, and Tubular Epithelial Cells in Sepsis-AKI.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 2;8:796724. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.796724. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34926535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

