PELP1/SRC-3-dependent regulation of metabolic PFKFB kinases drives therapy resistant ER+ breast cancer
- PMID: 34103681
- PMCID: PMC8238912
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-021-01871-w
PELP1/SRC-3-dependent regulation of metabolic PFKFB kinases drives therapy resistant ER+ breast cancer
Abstract
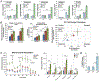
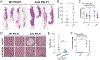
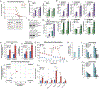
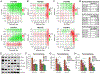
Recurrence of metastatic breast cancer stemming from acquired endocrine and chemotherapy resistance remains a health burden for women with luminal (ER+) breast cancer. Disseminated ER+ tumor cells can remain viable but quiescent for years to decades. Contributing factors to metastatic spread include the maintenance and expansion of breast cancer stem cells (CSCs). Breast CSCs frequently exist as a minority population in therapy resistant tumors. In this study, we show that cytoplasmic complexes composed of steroid receptor (SR) co-activators, PELP1 and SRC-3, modulate breast CSC expansion through upregulation of the HIF-activated metabolic target genes PFKFB3 and PFKFB4. Seahorse metabolic assays demonstrated that cytoplasmic PELP1 influences cellular metabolism by increasing both glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration. PELP1 interacts with PFKFB3 and PFKFB4 proteins, and inhibition of PFKFB3 and PFKFB4 kinase activity blocks PELP1-induced tumorspheres and protein-protein interactions with SRC-3. PFKFB4 knockdown inhibited in vivo emergence of circulating tumor cell (CTC) populations in mammary intraductal (MIND) models. Application of PFKFB inhibitors in combination with ER targeted therapies blocked tumorsphere formation in multiple models of advanced breast cancer including tamoxifen (TamR) and paclitaxel (TaxR) resistant models, murine tumor cells, and ER+ patient-derived organoids (PDxO). Together, our data suggest that PELP1, SRC-3, and PFKFBs cooperate to drive ER+ tumor cell populations that include CSCs and CTCs. Identifying non-ER pharmacological targets offers a useful approach to blocking metastatic escape from standard of care ER/estrogen (E2)-targeted strategies to overcome endocrine and chemotherapy resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Carol A. Lange is a Scientific Advisory Board Member for Context Therapeutics, Inc. Bryan E. Welm, Emilio Cortes-Sanchez, Katrin P. Guillen and Chieh-Hsiang Yang may receive financial compensation from intellectual property and tangible property licenses managed by the University of Utah. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in ER+ Breast Cancer Models Are Promoted by PELP1/AIB1 Complexes.Mol Cancer Res. 2018 Apr;16(4):707-719. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0598. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Mol Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29348189 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of ER-Src axis in hormonal therapy resistance.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Nov;130(2):377-85. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1312-2. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21184269 Free PMC article.
-
SETDB1 interactions with PELP1 contributes to breast cancer endocrine therapy resistance.Breast Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 8;24(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13058-022-01520-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35395812 Free PMC article.
-
PELP1: Structure, biological function and clinical significance.Gene. 2016 Jul 1;585(1):128-134. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.03.017. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26997260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocrine resistance in breast cancer.Climacteric. 2014 Oct;17(5):522-8. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2013.864268. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Climacteric. 2014. PMID: 24245601 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming in Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;15(13):3390. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133390. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-elemene Isopropanolamine Derivative LXX-8250 Induces Apoptosis Through Impairing Autophagic Flux via PFKFB4 Repression in Melanoma Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 10;13:900973. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.900973. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36034839 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of PFKFB4 by PIM2 promotes anaerobic glycolysis and cell proliferation in endometriosis.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 15;13(9):790. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05241-6. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36109523 Free PMC article.
-
AIB1/SRC-3/NCOA3 function in estrogen receptor alpha positive breast cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 30;14:1250218. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1250218. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37711895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic activation of PFKFB4 in breast tumor microenvironment shapes metabolic and cellular plasticity to accentuate metastatic competence.Cell Rep. 2022 Dec 6;41(10):111756. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111756. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36476868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vadlamudi RK, Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Kim Y, Shin J, Sahin A et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of PELP1, a novel human coregulator of estrogen receptor alpha. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 38272–38279. - PubMed
-
- Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Macmillan RD, Green AR et al. The prognostic significance of PELP1 expression in invasive breast cancer with emphasis on the ER-positive luminal-like subtype. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2010; 120: 603–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

