A 5-Year Retrospective Analysis of Raoultella planticola Bacteriuria
- PMID: 34103946
- PMCID: PMC8178696
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S306632
A 5-Year Retrospective Analysis of Raoultella planticola Bacteriuria
Abstract
Introduction: Raoultella planticola is an aerobic gram-negative rod predominantly found in soil and aquatic environments. The typical reservoirs of Raoultella spp. include the gastrointestinal tract and the upper respiratory tract. It usually causes pneumonia, biliary tract infections, and bacteremia. Urinary tract infection (UTI) secondary to R. planticola is an uncommon entity. Less than 10 cases of R. planticola-associated UTIs in adults have been published in the literature to date.
Objective: This is a single institution retrospective study undertaken to identify the epidemiology, patient characteristics, clinical spectrum, predisposing risk factors and the outcome of patients with UTI caused by R. planticola.
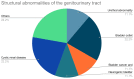
Results: A total of 37 R. planticola isolates were identified in urine samples over a 5-year study period. The mean age of the patient population was 77 years. The most common comorbidity was diabetes mellitus, which was present in 16 patients. Only 3 patients had a history of steroid use, an immunosuppressive condition, or were on chemotherapy. The most common presenting complaint was altered mental status followed by fever. Resistance to ampicillin was found in 35 isolates which seems to be an intrinsic characteristic of Raoultella spp. and 2 isolates were multidrug-resistant, but still susceptible to ciprofloxacin. The average length of stay was 3 days, and the average duration of antibiotic administration was 8 days. Ciprofloxacin was the most frequently prescribed antibiotic (9 patients). The severity of infection ranged from simple cystitis in 15 patients to urosepsis in 2 patients and septic shock in 2 patients. There were no mortalities in our cohort.
Conclusion: Our study revealed that patients with R. planticola UTI had higher proportion of diabetes mellitus, renal failure compared to the general population. Our study also confirms the intrinsic resistance to ampicillin of Raoultella spp., which has been documented previously in the literature.
Keywords: Raoultella; antibiotics; bacteriuria; infection; urinary tract infection.
© 2021 Alampoondi Venkataramanan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Castillo-Macías A, Flores-Aréchiga A, Llaca-Díaz J, Pérez-Chávez F, Casillas-Vega N. Microbiology of genus Raoultella, clinical features and difficulties in its diagnosis. Rev Medica Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2018;56(5):486–490. - PubMed
-
- Sękowska A. Raoultella spp.-clinical significance, infections and susceptibility to antibiotics. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2017;62(3):221–227. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous