Alcohol Ablation for Ventricular Tachycardia
- PMID: 34104316
- PMCID: PMC8158441
- DOI: 10.14797/NECT9586
Alcohol Ablation for Ventricular Tachycardia
Abstract
Catheter-based radiofrequency (RF) ablation is an effective, well-established therapy for ventricular tachycardia (VT). However, a large number of patients still have recurrences, particularly those with substrates arising from intramural locations that are inaccessible through endo- or epicardial catheter approaches. Several unconventional ablation techniques have been proposed to treat RF-refractory VT, including transarterial coronary ethanol ablation and retrograde coronary venous ethanol ablation. We review the evidence regarding the mechanisms, procedural aspects, and alcohol ablation outcomes for ventricular arrhythmias.
Keywords: LV summit; alcohol ablation; ventricular tachycardia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have completed and submitted the Methodist DeBakey Cardiovascular Journal Conflict of Interest Statement and none were reported.
Figures
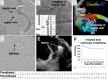
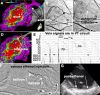
References
-
- Pedersen C T, Kay G N, Kalman J. EHRA/HRS/APHRS expert consensus on ventricular arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm. 2014;11(10) - PubMed
-
- Santangeli P, Marchlinski F E, Zado E S, et al. Percutaneous epicardial abla- tion of ventricular arrhythmias arising from the left ventricular summit: outcomes and electrocardiogram correlates of success. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2015;8(2):337–380. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.114.002377. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

