Simultaneous determination of five diuretic drugs using quantitative analysis of multiple components by a single marker
- PMID: 34108013
- PMCID: PMC8191180
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-021-00764-z
Simultaneous determination of five diuretic drugs using quantitative analysis of multiple components by a single marker
Abstract
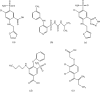
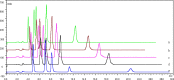
Background: Loop diuretics are commonly used in clinical practice to manage high fluid loads and to control fluid balance. In this paper, a novel quantitative analysis method for multiple components with a single marker (QAMS) was developed for the simultaneous determination of 5 diuretic drugs furosemide, torasemide, azosemide, etacrynic acid, and bumetanide, by HPLC. Qualitative analysis was performed using relative retention time and ultraviolet (UV) spectral similarity as the double indicator. The QAMS method was conducted with etacrynic acid as an internal reference substance. The quantities of the other four diuretics were calculated by using the relative correction factors for etacrynic acid. The quantities of the 5 diuretic drugs were also determined by the external standard method (ESM). Chromatographic separation was achieved on a Shimadzu HC-C18 column (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) using 50 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate (pH adjusted to 4.0 with phosphoric acid) with acetonitrile (64:36, v/v) as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min and a column temperature of 30 ℃.
Results: Under these conditions, the 5 diuretic drugs were well separated, showing linear relationships within certain ranges. The quantitative results showed that there was no significant difference between the QAMS and ESM methods.
Conclusions: Overall, the HPLC-QAMS analytical scheme established in this study is a simple, efficient, economical, and accurate method for the quantitative evaluation of 5 diuretic drugs.
Keywords: Diuretic drug; HPLC; Method development; Multi-components detection with a single marker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous determination of five nitroimidazole antimicrobials in pharmaceuticals using HPLC-ESM and QAMS methods.BMC Chem. 2025 Feb 14;19(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01409-1. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 39953570 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment of QAMS method with dehydroandrographolide as internal reference substance for quality control of Andrographis Herba].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Feb;44(4):730-739. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20181129.006. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30989886 Chinese.
-
Simultaneous Quantitative Analysis of Six Proton-Pump Inhibitors with a Single Marker and Evaluation of Stability of Investigated Drugs in Polypropylene Syringes for Continuous Infusion Use.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Dec 24;14:5689-5698. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S279302. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 33380789 Free PMC article.
-
[Simultaneous determination of glucosinolates and flavonoids in leaves of Moringa oleifera by quantitative analysis of multi-components by single-marker (QAMS)].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jun;47(12):3285-3294. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211214.203. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35851122 Chinese.
-
[Torasemide (LUPRAC): a review of its pharmacological and clinical profile].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 Aug;118(2):97-105. doi: 10.1254/fpj.118.97. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11530685 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Progress and prediction of multicomponent quantification in complex systems with practical LC-UV methods.J Pharm Anal. 2023 Feb;13(2):142-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2022.11.011. Epub 2022 Dec 5. J Pharm Anal. 2023. PMID: 36908853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous determination of five nitroimidazole antimicrobials in pharmaceuticals using HPLC-ESM and QAMS methods.BMC Chem. 2025 Feb 14;19(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01409-1. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 39953570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anisman SD, Erickson SB, Morden NE. How to prescribe loop diuretics in oedema. BMJ. 2019;364:1359. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
