Variant-specific inflation factors for assessing population stratification at the phenotypic variance level
- PMID: 34108454
- PMCID: PMC8190158
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23655-2
Variant-specific inflation factors for assessing population stratification at the phenotypic variance level
Abstract
In modern Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) epidemiological studies, participant-level data from multiple studies are often pooled and results are obtained from a single analysis. We consider the impact of differential phenotype variances by study, which we term 'variance stratification'. Unaccounted for, variance stratification can lead to both decreased statistical power, and increased false positives rates, depending on how allele frequencies, sample sizes, and phenotypic variances vary across the studies that are pooled. We develop a procedure to compute variant-specific inflation factors, and show how it can be used for diagnosis of genetic association analyses on pooled individual level data from multiple studies. We describe a WGS-appropriate analysis approach, implemented in freely-available software, which allows study-specific variances and thereby improves performance in practice. We illustrate the variance stratification problem, its solutions, and the proposed diagnostic procedure, in simulations and in data from the Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine Whole Genome Sequencing Program (TOPMed), used in association tests for hemoglobin concentrations and BMI.
Conflict of interest statement
Bruce M. Psaty serves on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
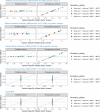
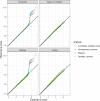
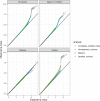

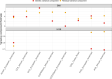
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201300049C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG059898/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL145425/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL098433/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300047C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300048C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300050C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135818/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072515/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL137181/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL066289/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100037C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL132825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States

