Comparative transcriptome analysis of inner blood-retinal barrier and blood-brain barrier in rats
- PMID: 34108511
- PMCID: PMC8190099
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91584-7
Comparative transcriptome analysis of inner blood-retinal barrier and blood-brain barrier in rats
Abstract
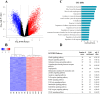
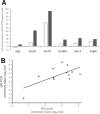
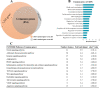
Although retinal microvessels (RMVs) and brain microvessels (BMVs) are closely related in their developmental and share similar blood-neural barriers, studies have reported markedly different responses to stressors such as diabetes. Therefore, we hypothesized that RMVs and BMVs will display substantial differences in gene expression levels even though they are of the same embryological origin. In this study, both RMVs and BMVs were mechanically isolated from rats. Full retinal and brain tissue samples (RT, BT) were collected for comparisons. Total RNA extracted from these four groups were processed on Affymetrix rat 2.0 microarray Chips. The transcriptional profiles of these tissues were then analyzed. In the present paper we looked at differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in RMVs (against RT) and BMVs (against BT) using a rather conservative threshold value of ≥ ± twofold change and a false discovery rate corrected for multiple comparisons (p < 0.05). In RMVs a total of 1559 DEGs were found, of which 1004 genes were higher expressed in RMVs than in RT. Moreover, 4244 DEGs between BMVs and BT were identified, of which 1956 genes were ≥ twofold enriched in BMVs. Using these DEGs, we comprehensively analyzed the actual expression levels and highlighted their involvement in critical functional structures in RMVs and BMVs, such as junctional complex, transporters and signaling pathways. Our work provides for the first time the transcriptional profiles of rat RMVs and BMVs. These results may help to understand why retina and brain microvasculature show different susceptibilities to stressors, and they might even provide new insight for pharmacological interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Responses of retinal and brain microvasculature to streptozotocin induced diabetes revealed by global expression profiling.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2023 Jan-Feb;20(1):14791641221147533. doi: 10.1177/14791641221147533. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2023. PMID: 36606460 Free PMC article.
-
A novel method to isolate retinal and brain microvessels from individual rats: Microscopic and molecular biological characterization and application in hyperglycemic animals.Vascul Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;110:24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Vascul Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30003960
-
Proteome profile differences among human, monkey, and mouse brain microvessels and cultured brain microvascular endothelial cells.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025 May 30;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12987-025-00650-z. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2025. PMID: 40448242 Free PMC article.
-
[Membrane Transporters and Their Regulatory Mechanisms at the Brain and Retinal Barriers to Establish Therapies for Refractory Central Nervous System Diseases].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020;140(10):1235-1242. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.20-00127. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 32999202 Review. Japanese.
-
[Carrier-mediated Transport of Cationic Drugs across the Blood-Tissue Barrier].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2015;135(10):1135-40. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.15-00181. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26423869 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Advances in brain barriers and brain fluids research in 2021: great progress in a time of adversity.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022 Jun 9;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12987-022-00343-x. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022. PMID: 35681151 Free PMC article.
-
C3a Mediates Endothelial Barrier Disruption in Brain-Derived, but Not Retinal, Human Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 19;25(20):11240. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011240. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457022 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring dysfunctional barrier phenotypes associated with glaucoma using a human pluripotent stem cell-based model of the neurovascular unit.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024 Nov 14;21(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12987-024-00593-x. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2024. PMID: 39543684 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Endothelial Cells: Heterogeneity and Targeting Approaches.Cells. 2021 Oct 10;10(10):2712. doi: 10.3390/cells10102712. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphine Accumulates in the Retina Following Chronic Systemic Administration.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 25;15(5):527. doi: 10.3390/ph15050527. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dosso AA, Leuenberger PM, Rungger-Brandle E. Remodeling of retinal capillaries in the diabetic hypertensive rat. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999;40:2405–2410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

