Quantitative proteomics identifies the core proteome of exosomes with syntenin-1 as the highest abundant protein and a putative universal biomarker
- PMID: 34108659
- PMCID: PMC9290189
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-021-00693-y
Quantitative proteomics identifies the core proteome of exosomes with syntenin-1 as the highest abundant protein and a putative universal biomarker
Abstract
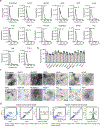
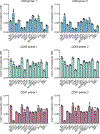
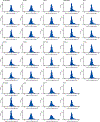
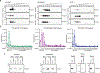
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles derived from the endosomal compartment that are potentially involved in intercellular communication. Here, we found that frequently used biomarkers of exosomes are heterogeneous, and do not exhibit universal utility across different cell types. To uncover ubiquitous and abundant proteins, we used an unbiased and quantitative proteomic approach based on super-stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (super-SILAC), coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. In total, 1,212 proteins were quantified in the proteome of exosomes, irrespective of the cellular source or isolation method. A cohort of 22 proteins was universally enriched. Fifteen proteins were consistently depleted in the proteome of exosomes compared to cells. Among the enriched proteins, we identified biogenesis-related proteins, GTPases and membrane proteins, such as CD47 and ITGB1. The cohort of depleted proteins in exosomes was predominantly composed of nuclear proteins. We identified syntenin-1 as a consistently abundant protein in exosomes from different cellular origins. Syntenin-1 is also present in exosomes across different species and biofluids, highlighting its potential use as a putative universal biomarker of exosomes. Our study provides a comprehensive quantitative atlas of core proteins ubiquitous to exosomes that can serve as a resource for the scientific community.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
MD Anderson Cancer Center and R.K. hold patents in the area of exosome biology and are licensed to Codiak Biosciences, Inc. MD Anderson Cancer Center and R.K. are stock equity holders in Codiak Biosciences, Inc. R.K. is a consultant and scientific adviser for Codiak Biosciences, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
-
- Colombo M, Raposo G & Thery C Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30, 255–289 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G & Thery C Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol 21, 9–17 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

