Aggressive Hydration With Ringer's Lactate in the Prevention of Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34109084
- PMCID: PMC8180436
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14897
Aggressive Hydration With Ringer's Lactate in the Prevention of Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) pancreatitis (PEP) is a dangerous complication and occurs in a considerable number of patients. However, since well-randomized controlled trials investigating aggressive hydration with Ringer's lactate are lacking, this meta-analysis assessed the role of aggressive hydration with Ringer's lactate alone or in combination with other therapies in the prevention of PEP. We searched PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar for relevant articles. The search engine was set to randomize controlled trials and prospective cohorts assessing Ringer's lactate in PEP prevention either alone or in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and stent. The keywords "aggressive hydration," "Ringer's lactate," "post-ERCP pancreatitis," "NSAIDs," "stent placement," and "somatostatin analogs" were used. The search was limited to a study on humans published in English with no limitation to the study period. Two hundred and six articles were retrieved. Only eight articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria. The studies showed a reduction of post-ERCP pancreatitis using aggressive hydration with Ringer's lactate alone (odds ratio 0.23, 95% CI 0.13 - 0.40, P-value < 0.001, I2 for heterogeneity = 0%, P-value = 0.61, Chi-square value 1.83, and degrees of freedom (df) 3. In addition, the combination of Ringer's lactate with stents or NSAIDs was superior to Ringer's lactate alone (odds ratio 0.63, 95% CI 0.41 - 0.98, P-value < 0.04, I2 for heterogeneity = 0%, P-value = 0.48, Chi-square value 2.47, and df 3). Aggressive hydration with Ringer's lactate alone was effective in the prevention of PEP with a superior effect when combined with stents and NSAIDs.
Keywords: aggressive hydration; endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ercp); post-ercp pancreatitis (pep); ringer's lactate.
Copyright © 2021, Aljohani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
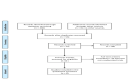


Similar articles
-
Aggressive fluid hydration plus non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs versus non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs alone for post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis (FLUYT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled trial.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;6(5):350-358. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00057-1. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33740415 Clinical Trial.
-
Aggressive hydration compared to standard hydration with lactated ringer's solution for prevention of post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis.Surg Endosc. 2021 Mar;35(3):1126-1137. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-07477-9. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Surg Endosc. 2021. PMID: 32140860
-
Aggressive hydration with lactated Ringer's solution reduces pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Feb;12(2):303-7.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.07.026. Epub 2013 Aug 3. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 23920031 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, intravenous fluids, pancreatic stents, or their combinations for the prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Sep;6(9):733-742. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00170-9. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34214449
-
Aggressive hydration with lactated ringer solution in prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Apr 23;100(16):e25598. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025598. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33879722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The past, present, and future of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Kozarek RA. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5718180/ Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2017;13:620–622. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ringer's lactate hydration and incidence of post ERCP pancreatitis: a descriptive cross-sectional study. Pun A, Dhungana A, Neupane D. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7580329/ JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2020;58:645–649. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Positive correlation between pancreatic volume and post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis. Maruyama H, Shiba M, Ishikawa-Kakiya Y, et al. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;35:769–776. - PubMed
-
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs alleviate severity of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis by inhibiting inflammation and reducing apoptosis. Geng C, Li X, Li Y, Song S, Wang C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;35:896–904. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
