PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP2C9
- PMID: 34109627
- PMCID: PMC8607432
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.2333
PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP2C9
Abstract
The Pharmacogene Variation Consortium (PharmVar) catalogues star (*) allele nomenclature for the polymorphic human CYP2C9 gene. Genetic variation within the CYP2C9 gene locus impacts the metabolism or bioactivation of many clinically important drugs, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, phenytoin, antidiabetic agents, and angiotensin receptor blockers. Variable CYP2C9 activity is of particular importance regarding efficacy and safety of warfarin and siponimod as indicated in their package inserts. This GeneFocus provides a comprehensive overview and summary of CYP2C9 and describes how haplotype information catalogued by PharmVar is utilized by the Pharmacogenomics Knowledgebase and the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics © 2021 American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
Indiana University School of Medicine Pharmacogenomics Laboratory is a fee-for-service clinical laboratory that offers clinical pharmacogenetic testing. A.L.D. is a paid employee of Acadia Pharmaceuticals; S.A.S. is a paid consultant of Sema4. All other authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures


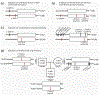
 ) symbol indicates that a core SNV alters function and the PharmVar (
) symbol indicates that a core SNV alters function and the PharmVar ( ) symbol highlights that a core SNV is unique to a star allele. SNV positions refer to the transcript (NM_000771.4).
) symbol highlights that a core SNV is unique to a star allele. SNV positions refer to the transcript (NM_000771.4).
References
-
- Scott J & Poffenbarger PL Pharmacogenetics of tolbutamide metabolism in humans. Diabetes 28, 41–51 (1979). - PubMed
-
- Miners JO, Wing LM & Birkett DJ Normal metabolism of debrisoquine and theophylline in a slow tolbutamide metaboliser. Aust N Z J Med 15, 348–9 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Yasumori T, Kawano S, Nagata K, Shimada M, Yamazoe Y & Kato R Nucleotide sequence of a human liver cytochrome P-450 related to the rat male specific form. J Biochem 102, 1075–82 (1987). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

