New Insights into the Critical Importance of Intratubular Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications in Hypertension
- PMID: 34110521
- PMCID: PMC8314783
- DOI: 10.1007/s11906-021-01152-7
New Insights into the Critical Importance of Intratubular Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications in Hypertension
Abstract
Purpose of review: The sodium (Na+) and hydrogen (H+) exchanger 3 (NHE3), known as solute carrier family 9 member 3 (SLC9A3), mediates active transcellular Na+ and bicarbonate reabsorption in the small intestine of the gut and proximal tubules of the kidney. The purpose of this article is to review and discuss recent findings on the critical roles of intestinal and proximal tubule NHE3 in maintaining basal blood pressure (BP) homeostasis and their potential therapeutic implications in the development of angiotensin II (Ang II)-dependent hypertension.
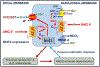
Recent findings: Recently, our and other laboratories have generated or used novel genetically modified mouse models with whole-body, kidney-specific, or proximal tubule-specific deletion of NHE3 to determine the critical roles and underlying mechanisms of NHE3 in maintaining basal BP homeostasis and the development of Ang II-induced hypertension at the whole-body, kidney, or proximal tubule levels. The new findings demonstrate that NHE3 contributes to about 10 to 15 mmHg to basal blood pressure levels, and that deletion of NHE3 at the whole-kidney or proximal tubule level, or pharmacological inhibition of NHE3 at the kidney level with an orally absorbable NHE3 inhibitor AVE-0657, attenuates ~ 50% of Ang II-induced hypertension in mice. The results support the proof-of-concept hypothesis that NHE3 plays critical roles in physiologically maintaining normal BP and in the development of Ang II-dependent hypertension. Our results also strongly suggest that NHE3 in the proximal tubules of the kidney may be therapeutically targeted to treat poorly controlled hypertension in humans.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Blood pressure; Hypertension; Na+/H+ exchanger 3; Proximal tubule.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Proximal Tubule-Specific Deletion of the NHE3 (Na+/H+ Exchanger 3) in the Kidney Attenuates Ang II (Angiotensin II)-Induced Hypertension in Mice.Hypertension. 2019 Sep;74(3):526-535. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13094. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31352824 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and genomic evidence for an important role of the Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in blood pressure regulation and angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Physiol Genomics. 2019 Apr 1;51(4):97-108. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00122.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Physiol Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30849009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 in the Intestines and the Proximal Tubule of the Kidney: Localization, Physiological Function, and Key Roles in Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension.Front Physiol. 2022 Apr 19;13:861659. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.861659. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35514347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II and AT1a Receptors in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney: New Roles in Blood Pressure Control and Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 22;23(5):2402. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052402. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Deletion of AT1a Receptor or Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Selectively in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney Attenuates Two-Kidney, One-Clip Goldblatt Hypertension in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15798. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415798. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555438 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kidney and blood pressure regulation-latest evidence for molecular mechanisms.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Jan 24;16(6):952-964. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad015. eCollection 2023 Jun. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 37261007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal autocrine neuropeptide FF (NPFF) signaling regulates blood pressure.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 4;14(1):15407. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64484-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38965251 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of thick ascending limb and distal convoluted tubule to glucose-induced hypercalciuria in healthy controls.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):F811-F816. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00130.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37823200 Free PMC article.
-
The Remaining Conundrum of the Role of the Na+/H+ Exchanger Isoform 1 (NHE1) in Cardiac Physiology and Pathology: Can It Be Rectified?Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 15;23(8):284. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2308284. eCollection 2022 Aug. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39076631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Detection of pathogenic gene mutations in thirteen cases of congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens infertility patients].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Oct 18;56(5):763-774. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.003. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39397452 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018; 71(6):e13–e115. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, et al. Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2008; 51(6): 1403–19. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De SG, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010; 121(7):e46–215. - PubMed
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial. Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA. 2002; 288(23):2981–97. - PubMed
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, DennisonHimmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014; 311(5):507–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

