Vascular Impact of Cancer Therapies: The Case of BTK (Bruton Tyrosine Kinase) Inhibitors
- PMID: 34110908
- PMCID: PMC10185355
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318259
Vascular Impact of Cancer Therapies: The Case of BTK (Bruton Tyrosine Kinase) Inhibitors
Abstract
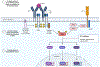
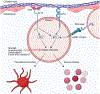
Novel targeted cancer therapies have revolutionized oncology therapies, but these treatments can have cardiovascular complications, which include heterogeneous cardiac, metabolic, and vascular sequelae. Vascular side effects have emerged as important considerations in both cancer patients undergoing active treatment and cancer survivors. Here, we provide an overview of vascular effects of cancer therapies, focusing on small-molecule kinase inhibitors and specifically inhibitors of BTK (Bruton tyrosine kinase), which have revolutionized treatment and prognosis for B-cell malignancies. Cardiovascular side effects of BTK inhibitors include atrial fibrillation, increased risk of bleeding, and hypertension, with the former 2 especially providing a treatment challenge for the clinician. Cardiovascular complications of small-molecule kinase inhibitors can occur through either on-target (targeting intended target kinase) or off-target kinase inhibition. We will review these concepts and focus on the case of BTK inhibitors, highlight the emerging data suggesting an off-target effect that may provide insights into development of arrhythmias, specifically atrial fibrillation. We believe that cardiac and vascular sequelae of novel targeted cancer therapies can provide insights into human cardiovascular biology.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; cancer survivors; hypertension; prognosis; protein-tyrosine kinases.
Figures

References
-
- Moslehi JJ. Cardiovascular Toxic Effects of Targeted Cancer Therapies. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1457–1467. - PubMed
-
- Jaiswal S, Fontanillas P, Flannick J, Manning A, Grauman PV, Mar BG, Lindsley RC, Mermel CH, Burtt N, Chavez A, Higgins JM, Moltchanov V, Kuo FC, Kluk MJ, Henderson B, Kinnunen L, Koistinen HA, Ladenvall C, Getz G, Correa A, Banahan BF, Gabriel S, Kathiresan S, Stringham HM, McCarthy MI, Boehnke M, Tuomilehto J, Haiman C, Groop L, Atzmon G, Wilson JG, Neuberg D, Altshuler D and Ebert BL. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2488–98. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Sidlow R, Lin AE, Gupta D, Jones LW, Moslehi J, Zeiher A, Jaiswal S, Schulz C, Blankstein R, Bolton KL, Steensma D, Levine RL and Ebert BL. Clonal Hematopoiesis: Crossroads of Aging, Cardiovascular Disease, and Cancer: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:567–577. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meijers WC, Maglione M, Bakker SJL, Oberhuber R, Kieneker LM, de Jong S, Haubner BJ, Nagengast WB, Lyon AR, van der Vegt B, van Veldhuisen DJ, Westenbrink BD, van der Meer P, Sillje HHW and de Boer RA. Heart Failure Stimulates Tumor Growth by Circulating Factors. Circulation. 2018;138:678–691. - PubMed

