Effects of Jian Pi Qing Chang Hua Shi decoction on mucosal injuries in a 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid-induced inflammatory bowel disease rat model
- PMID: 34110957
- PMCID: PMC8204966
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1928240
Effects of Jian Pi Qing Chang Hua Shi decoction on mucosal injuries in a 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid-induced inflammatory bowel disease rat model
Abstract
Context: Jian Pi Qing Chang Hua Shi decoction (JPQCHSD) has been considered as an effective remedy for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Chinese traditional medicine.
Objective: We evaluated the efficacy of JPQCHSD on 2-4-6-trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (TNBS)-induced IBD rats and the responsible mechanisms.
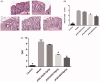
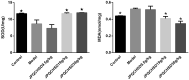
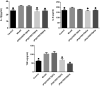
Materials and methods: Except the rats of the control group (50% ethanol), Sprague-Dawley rats (180 ± 20 g) induced by TNBS (150 mg/kg in 50% ethanol), received water extract of JPQCHSD daily at 0, 9.5, 19, or 38 g/kg for 12 days. The rats were sacrificed, and their colons were removed to evaluate the disease activity index. Malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), myeloperoxidase (MPO), immunoglobulin A (IgA), tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and nuclear factor-κB were evaluated.
Results: JPQCHSD extract significantly reduced the disease activity index of TNBS-induced colitis with a median effective dose (ED50) of 26.93 g/kg. MPO and MDA were significantly reduced in the 19 and 38 g/kg groups (ED50 values 37.38 and 53.2 g/kg, respectively). The ED50 values for the increased SOD and IgA were 48.98 and 56.3 g/kg. ED50 values for inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 were 32.66, 75.72, and 162.06 g/kg, respectively.
Discussion: JPQCHSD promoted mucosal healing in IBD rats via its anti-inflammation, immune regulation, and antioxidation properties.
Conclusions: JPQCHSD has healing function on IBD. Further clinical trials are needed to demonstrate its efficacy and tolerance to IBD.
Keywords: Superoxide dismutase; immunoglobulin A; interleukin-1β; malondialdehyde; myeloperoxidase; nuclear factor-κB; tumour necrosis factor-α.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests regarding this manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Casearia sylvestris var. lingua (Càmbess.) Eichler leaves aqueous extract improves colon inflammation through mucogenic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions in TNBS- induced IBD rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Oct 5;332:118393. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118393. Epub 2024 May 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38801913
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of Chang-An-Shuan on TNBS-induced experimental colitis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jun 15;17(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1794-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28619075 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and histopathological evidence on the beneficial effects of Tragopogon graminifolius in TNBS-induced colitis.Pharm Biol. 2015 Mar;53(3):429-36. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.923004. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Pharm Biol. 2015. PMID: 25471611
-
Efficacy of thalidomide on trinitrobenzene sulfonate-induced colitis in young rats and its mechanism.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(12):2368-75. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 24931258
-
Resveratrol for inflammatory bowel disease in preclinical studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 14;15:1411566. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1411566. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38948464 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of vitamin D3 and a stinging nettle extract on the gastric tissue of rats administered with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid.Vet Med (Praha). 2024 Mar 28;69(3):84-93. doi: 10.17221/111/2023-VETMED. eCollection 2024 Mar. Vet Med (Praha). 2024. PMID: 38623153 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the immunity and inflammation by autophagy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Jul 2;4(4):e311. doi: 10.1002/mco2.311. eCollection 2023 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37405276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of Youhua Kuijie Prescription and sulfasalazine can alleviate experimental colitis via IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 10;15:1437503. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1437503. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39318778 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Tiaoganquzhi Decoction in Treating inflammatory Injury of Nonalcoholic Fatty liver Disease by Promoting CGI-58 and Inhibiting Expression of NLRP3 Inflammasome.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 2;13:851267. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.851267. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35586044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akanda MR, Nam HH, Tian W, Islam A, Choo BK, Park BY.. 2018. Regulation of JAK2/STAT3 and NF-κB signal transduction pathways; Veronica polita alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 100:296–303. - PubMed
-
- Babbs CF. 1992. Oxygen radicals in ulcerative colitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 13(2):169–181. - PubMed
-
- Bamba T, Yamamoto T, Umegae S, Matsumoto K.. 2014. Effects of preoperative leukocytapheresis on inflammatory cytokines following surgery for ulcerative colitis: a prospective randomized study. J Clin Apher. 29(2):107–112. - PubMed
-
- Barnes EL, Lightner AL, Regueiro M.. 2020. Perioperative and postoperative management of patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18(6):1356–1366. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
