The functional role of sequentially neuromodulated synaptic plasticity in behavioural learning
- PMID: 34111110
- PMCID: PMC8192019
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009017
The functional role of sequentially neuromodulated synaptic plasticity in behavioural learning
Abstract
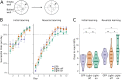
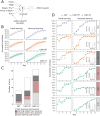
To survive, animals have to quickly modify their behaviour when the reward changes. The internal representations responsible for this are updated through synaptic weight changes, mediated by certain neuromodulators conveying feedback from the environment. In previous experiments, we discovered a form of hippocampal Spike-Timing-Dependent-Plasticity (STDP) that is sequentially modulated by acetylcholine and dopamine. Acetylcholine facilitates synaptic depression, while dopamine retroactively converts the depression into potentiation. When these experimental findings were implemented as a learning rule in a computational model, our simulations showed that cholinergic-facilitated depression is important for reversal learning. In the present study, we tested the model's prediction by optogenetically inactivating cholinergic neurons in mice during a hippocampus-dependent spatial learning task with changing rewards. We found that reversal learning, but not initial place learning, was impaired, verifying our computational prediction that acetylcholine-modulated plasticity promotes the unlearning of old reward locations. Further, differences in neuromodulator concentrations in the model captured mouse-by-mouse performance variability in the optogenetic experiments. Our line of work sheds light on how neuromodulators enable the learning of new contingencies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/P019560/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 200790/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/N019008/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/N013956/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

