Characterization of a Novel Caveolin Modulator That Reduces Vascular Permeability and Ocular Inflammation
- PMID: 34111267
- PMCID: PMC8132009
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.10.6.21
Characterization of a Novel Caveolin Modulator That Reduces Vascular Permeability and Ocular Inflammation
Abstract
Purpose: Caveolin (Cav) regulates various aspect of endothelial cell signaling and cell-permeable peptides (CPPs) fused to domains of Cav can reduce retinal damage and inflammation in vivo. Thus, the goal of the present study was to identify a novel CPP that improves delivery of a truncated Cav modulator in vitro and in vivo.
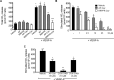
Methods: Phage display technology was used to identify a small peptide (RRPPR) that was internalized into endothelial cells. Fusions of Cav with the peptide were compared to existing molecules in three distinct assays, vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF) induced nitric oxide (NO) release, VEGF induced vascular leakage, and in a model of immune mediated uveitis.
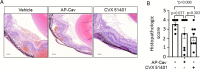
Results: RRPPR was internalized efficiently and was potent in blocking NO release. Fusing RRPPR with a minimal Cav inhibitory domain (CVX51401) dose-dependently blocked NO release, VEGF induced permeability, and retinal damage in a model of uveitis.
Conclusions: CVX51401 is a novel Cav modulator that reduces VEGF and immune mediated inflammation.
Translational relevance: CVX51401 is an optimized Cav modulator that reduces vascular permeability and ocular inflammation that is poised for clinical development.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


References
-
- Kardani K, Milani A, Shabani SH, Bolhassani A. Cell penetrating peptides: the potent multi-cargo intracellular carriers. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019; 16: 1227–1258. - PubMed
-
- Derossi D, Joliot AH, Chassaing G, Prochiantz A. The third helix of the Antennapedia homeodomain translocates through biological membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994; 269: 10444–10450. - PubMed
-
- Vives E, Brodin P, Lebleu B. A truncated HIV-1 Tat protein basic domain rapidly translocates through the plasma membrane and accumulates in the cell nucleus. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272: 16010–16017. - PubMed
-
- Bucci M, Gratton JP, Rudic RD, et al. .. In vivo delivery of the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain inhibits nitric oxide synthesis and reduces inflammation. Nat Med. 2000; 6: 1362–1367. - PubMed
-
- Gratton JP, Lin MI, Yu J, et al. .. Selective inhibition of tumor microvascular permeability by cavtratin blocks tumor progression in mice. Cancer Cell 2003; 4: 31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

