Spinal microglial β-endorphin signaling mediates IL-10 and exenatide-induced inhibition of synaptic plasticity in neuropathic pain
- PMID: 34111331
- PMCID: PMC8446220
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13694
Spinal microglial β-endorphin signaling mediates IL-10 and exenatide-induced inhibition of synaptic plasticity in neuropathic pain
Abstract
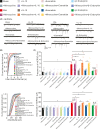
Aim: This study aimed to investigate the regulation of pain hypersensitivity induced by the spinal synaptic transmission mechanisms underlying interleukin (IL)-10 and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist exenatide-induced pain anti-hypersensitivity in neuropathic rats through spinal nerve ligations.
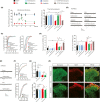
Methods: Neuropathic pain model was established by spinal nerve ligation of L5/L6 and verified by electrophysiological recording and immunofluorescence staining. Microglial expression of β-endorphin through autocrine IL-10- and exenatide-induced inhibition of glutamatergic transmission were performed by behavioral tests coupled with whole-cell recording of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) and miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) through application of endogenous and exogenous IL-10 and β-endorphin.
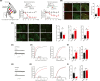
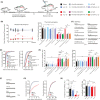
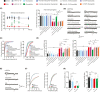
Results: Intrathecal injections of IL-10, exenatide, and the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonists β-endorphin and DAMGO inhibited thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in neuropathic rats. Whole-cell recordings of bath application of exenatide, IL-10, and β-endorphin showed similarly suppressed enhanced frequency and amplitude of the mEPSCs in the spinal dorsal horn neurons of laminae II, but did not reduce the frequency and amplitude of mIPSCs in neuropathic rats. The inhibitory effects of IL-10 and exenatide on pain hypersensitive behaviors and spinal synaptic plasticity were totally blocked by pretreatment of IL-10 antibody, β-endorphin antiserum, and MOR antagonist CTAP. In addition, the microglial metabolic inhibitor minocycline blocked the inhibitory effects of IL-10 and exenatide but not β-endorphin on spinal synaptic plasticity.
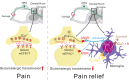
Conclusion: This suggests that spinal microglial expression of β-endorphin mediates IL-10- and exenatide-induced inhibition of glutamatergic transmission and pain hypersensitivity via presynaptic and postsynaptic MORs in spinal dorsal horn.
Keywords: IL-10; Neuropathic pain; exenatide; mEPSCs; mIPSCs; microglia; β-endorphin.
© 2021 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microglial Activation of GLP-1R Signaling in Neuropathic Pain Promotes Gene Expression Adaption Involved in Inflammatory Responses.Neural Plast. 2021 Aug 31;2021:9923537. doi: 10.1155/2021/9923537. eCollection 2021. Neural Plast. 2021. PMID: 34512747 Free PMC article.
-
Shanzhiside methylester, the principle effective iridoid glycoside from the analgesic herb Lamiophlomis rotata, reduces neuropathic pain by stimulating spinal microglial β-endorphin expression.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Feb;101:98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26363192
-
Autocrine Interleukin-10 Mediates Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor-Induced Spinal Microglial β-Endorphin Expression.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 29;37(48):11701-11714. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1799-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29084866 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Molecular and Synaptic Targets for the Management of Chronic Pain Caused by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 22;25(7):3602. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073602. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinal inhibitory neurotransmission in neuropathic pain.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2009 Jun;13(3):208-14. doi: 10.1007/s11916-009-0035-8. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2009. PMID: 19457281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha 2-adrenoceptor participates in anti-hyperalgesia by regulating metabolic demand.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1359319. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1359319. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38584597 Free PMC article.
-
Store-operated calcium entry mediates hyperalgesic responses during neuropathy.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Nov;13(11):2020-2034. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13699. Epub 2023 Aug 28. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 37606998 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in the Regulation of Interleukins in Chronic Pain: A Widely Recognized but Difficult-to-Tackle Factor.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 18;26(8):3835. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083835. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Intestinal Enteroendocrine Cells in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 14;10(10):2577. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102577. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 in the spinal dorsal horn ameliorates neuropathic pain via cAMP-cytokine-Cx43 signaling in mice.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 May;28(5):749-760. doi: 10.1111/cns.13807. Epub 2022 Feb 14. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35156776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takasugi Y, Iwamoto T, Fuyuta M, Koga Y, Tabuchi M, Higashino H. Suppression of the descending inhibitory pathway by continuous thoracic intrathecal lidocaine infusion reduces the thermal threshold of the tail‐flick response in rats. J Anesth. 2009;23(3):399‐402. 10.1007/s00540-009-0767-y - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

