Potential of AKT2 expression as a predictor of lymph-node metastasis in invasive breast carcinoma of no special type
- PMID: 34111909
- PMCID: PMC8353139
- DOI: 10.4132/jptm.2021.04.26
Potential of AKT2 expression as a predictor of lymph-node metastasis in invasive breast carcinoma of no special type
Abstract
Background: Invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST) is the most common type of breast cancer and mainly causes regional lymph-node metastasis (LNM). We investigated the potential for AKT2 expression as a predictive biomarker for LNM in IBC-NST.
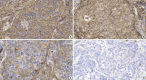
Methods: Forty-eight paraffin blocks containing IBC-NST primary tumors were divided into two groups based on presence or absence of LNM. Age, tumor grade, tumor size, lymphovascular invasion (LVI), and AKT expression were assessed. AKT2 expression was assessed based on immunohistochemical staining, while other data were collected from archives.
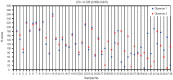
Results: Multiple logistic regression results showed that AKT2 expression and LVI were significantly associated with LNM (odds ratio [OR], 5.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.42 to 19.93 and OR, 4.46; 95% CI, 1.17 to 16.97, respectively). AKT2 expression was able to discriminate against LNM (area under the receiver operating characteristic, 0.799 ± 0.063; 95% CI, 0.676 to 0.921) at an H-score cutoff of 104.62 (83.3% sensitivity, 62.5% specificity).
Conclusions: AKT2 expression has potential as a predictor of LNM in IBC-NST. The H-score cutoff for AKT2 expression can be used as a classification guide in future studies.
Keywords: AKT2; Breast neoplasms; Immunohistochemistry; Metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram IS, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Song M, Bode AM, Dong Z, Lee MH. AKT as a therapeutic target for cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79:1019–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

