Systematic review and narrative synthesis of suicide prevention in high-schools and universities: a research agenda for evidence-based practice
- PMID: 34112141
- PMCID: PMC8194002
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-11124-w
Systematic review and narrative synthesis of suicide prevention in high-schools and universities: a research agenda for evidence-based practice
Abstract
Background: Youth suicide prevention in high-schools and universities is a public health priority. Our aim was to propose a research agenda to advance evidence-based suicide prevention in high-schools and universities by synthesizing and critically reviewing the research focus and methodologies used in existing intervention studies.
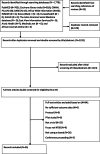
Methods: Fourteen databases were systematically searched to identify studies which evaluate suicide prevention interventions delivered on high-school or university campuses, with before and after measures. Data from included studies (n = 43) were extracted to identify what, where, how and for whom interventions have been tested. Narrative synthesis was used to critically evaluate research focus and methodology. Study quality was assessed.
Results: Research has focused primarily on selective interventions, with less attention on indicated and universal interventions. Most evidence comes from North America and high-income countries. The target of interventions has been: non-fatal suicidal behaviour; confidence and ability of staff/students to intervene in a suicidal crisis; suicide-related knowledge and attitudes; and suicide-related stigma. No studies included suicide deaths as an outcome, evaluated eco-systemic interventions, explored how context influences implementation, used multisite study designs, or focused explicitly on LGBTQ+ youth. Two studies evaluated digital interventions. Quality of the majority of studies was compromised by lack of methodological rigour, small samples, and moderate/high risk of bias. Interventions often assume the existence of an external well-functioning referral pathway, which may not be true in low-resource settings.
Conclusion: To advance evidence-based suicide prevention in educational settings we need to: conduct more high-quality clinical and pragmatic trials; promote research in low- and middle-income countries; test targeted interventions for vulnerable populations (like LGBTQ+ youth), evaluate interventions where death by suicide is the primary outcome; include translational studies and use implementation science to promote intervention uptake; evaluate the potential use of digital and eco-systemic interventions; and conduct multisite studies in diverse cultural settings.
Keywords: Campus-based; High-school; Prevention interventions; Students; Suicide prevention; University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
References
-
- World Health Organisation . Surveillance of suicide and suicide attempts. 2017. p. 2017.
-
- Auerbach RP, Mortier P, Bruffaerts R, Alonso J, Benjet C, Cuijpers P, Demyttenaere K, Ebert DD, Green JG, Hasking P, Murray E, Nock MK, Pinder-Amaker S, Sampson NA, Stein DJ, Vilagut G, Zaslavsky AM, Kessler RC, WHO WMH-ICS Collaborators WHO world mental health surveys international college student project: prevalence and distribution of mental disorders. J Abnorm Psychol. 2018;127(7):623–638. doi: 10.1037/abn0000362. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical