Differential Effects of the Six Human TAU Isoforms: Somatic Retention of 2N-TAU and Increased Microtubule Number Induced by 4R-TAU
- PMID: 34113229
- PMCID: PMC8185039
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.643115
Differential Effects of the Six Human TAU Isoforms: Somatic Retention of 2N-TAU and Increased Microtubule Number Induced by 4R-TAU
Abstract
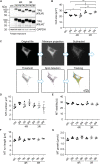
In the adult human brain, six isoforms of the microtubule-associated protein TAU are expressed, which result from alternative splicing of exons 2, 3, and 10 of the MAPT gene. These isoforms differ in the number of N-terminal inserts (0N, 1N, 2N) and C-terminal repeat domains (3R or 4R) and are differentially expressed depending on the brain region and developmental stage. Although all TAU isoforms can aggregate and form neurofibrillary tangles, some tauopathies, such as Pick's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy, are characterized by the accumulation of specific TAU isoforms. The influence of the individual TAU isoforms in a cellular context, however, is understudied. In this report, we investigated the subcellular localization of the human-specific TAU isoforms in primary mouse neurons and analyzed TAU isoform-specific effects on cell area and microtubule dynamics in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Our results show that 2N-TAU isoforms are particularly retained from axonal sorting and that axonal enrichment is independent of the number of repeat domains, but that the additional repeat domain of 4R-TAU isoforms results in a general reduction of cell size and an increase of microtubule counts in cells expressing these specific isoforms. Our study points out that individual TAU isoforms may influence microtubule dynamics differentially both by different sorting patterns and by direct effects on microtubule dynamics.
Keywords: MAPT; SH-SY5Y cell line; TAU; axonal targeting; microtubule dynamics; microtubule-associated proteins; primary neuron cell culture; somatodendritic localization.
Copyright © 2021 Bachmann, Bell, Klimek and Zempel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Arai T., Ikeda K., Akiyama H., Tsuchiya K., Iritani S., Ishiguro K., et al. (2003). Different immunoreactivities of the microtubule-binding region of tau and its molecular basis in brains from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, Pick’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 105 489–498. 10.1007/s00401-003-0671-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beevers J. E., Lai M. C., Collins E., Booth H. D. E., Zambon F., Parkkinen L., et al. (2017). MAPT Genetic Variation and Neuronal Maturity Alter Isoform Expression Affecting Axonal Transport in iPSC-Derived Dopamine Neurons. Stem Cell Rep. 9 587–599. 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.06.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

