Dermatan Sulfate Is a Potential Regulator of IgH via Interactions With Pre-BCR, GTF2I, and BiP ER Complex in Pre-B Lymphoblasts
- PMID: 34113352
- PMCID: PMC8185350
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.680212
Dermatan Sulfate Is a Potential Regulator of IgH via Interactions With Pre-BCR, GTF2I, and BiP ER Complex in Pre-B Lymphoblasts
Abstract
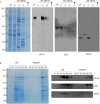
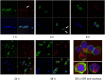
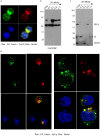
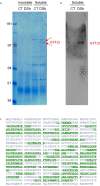
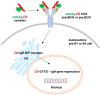
Dermatan sulfate (DS) and autoantigen (autoAg) complexes are capable of stimulating autoreactive CD5+ B1 cells. We examined the activity of DS on CD5+ pre-B lymphoblast NFS-25 cells. CD19, CD5, CD72, PI3K, and Fas possess varying degrees of DS affinity. The three pre-BCR components, Ig heavy chain mu (IgH), VpreB, and lambda 5, display differential DS affinities, with IgH having the strongest affinity. DS attaches to NFS-25 cells, gradually accumulates in the ER, and eventually localizes to the nucleus. DS and IgH co-localize on the cell surface and in the ER. DS associates strongly with 17 ER proteins (e.g., BiP/Grp78, Grp94, Hsp90ab1, Ganab, Vcp, Canx, Kpnb1, Prkcsh, Pdia3), which points to an IgH-associated multiprotein complex in the ER. In addition, DS interacts with nuclear proteins (Ncl, Xrcc6, Prmt5, Eftud2, Supt16h) and Lck. We also discovered that DS binds GTF2I, a required gene transcription factor at the IgH locus. These findings support DS as a potential regulator of IgH in pre-B cells at protein and gene levels. We propose a (DS•autoAg)-autoBCR dual signal model in which an autoBCR is engaged by both autoAg and DS, and, once internalized, DS recruits a cascade of molecules that may help avert apoptosis and steer autoreactive B cell fate. Through its affinity with autoAgs and its control of IgH, DS emerges as a potential key player in the development of autoreactive B cells and autoimmunity.
Keywords: BiP; GTF2I; Ig heavy chain; autoimmunity; dermatan sulfate (DS); precursor BCR.
Copyright © 2021 Lee, Rho, Roehrl and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
JR is employed by MP Biomedicals New Zealand Ltd. MR is on the scientific advisory boards of Trans-Hit, Proscia, and Universal DX. JW is the founder of Curandis. None of these companies had influence on the design, interpretation, or decision to publish of this study. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of B lymphocyte antigen receptor polypeptides with multiple chaperone proteins.Immunol Lett. 2001 Oct 1;78(3):149-60. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(01)00256-5. Immunol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11578689
-
Immunoglobulin mu heavy chains do not mediate tyrosine phosphorylation of Ig alpha from the ER-cis-Golgi.J Immunol. 2003 Sep 15;171(6):3091-101. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3091. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12960335
-
Role of the Igh intronic enhancer Eμ in clonal selection at the pre-B to immature B cell transition.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 15;191(8):4399-411. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301858. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24058175 Free PMC article.
-
The pre-B cell receptor and its role in proliferation and Ig heavy chain allelic exclusion.Semin Immunol. 2002 Oct;14(5):335-42. doi: 10.1016/s1044-5323(02)00066-0. Semin Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12220934 Review.
-
Repertoire selection by pre-B-cell receptors and B-cell receptors, and genetic control of B-cell development from immature to mature B cells.Immunol Rev. 2000 Jun;175:33-46. Immunol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10933589 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycoprotein α-Subunit of Glucosidase II (GIIα) is a novel prognostic biomarker correlated with unfavorable outcome of urothelial carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jul 25;22(1):817. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09884-8. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35879690 Free PMC article.
-
An Autoantigen Atlas from Human Lung HFL1 Cells Offers Clues to Neurological and Diverse Autoimmune Manifestations of COVID-19.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jan 24:2021.01.24.427965. doi: 10.1101/2021.01.24.427965. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 24;13:831849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.831849. PMID: 33501444 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
An Autoantigen Profile of Human A549 Lung Cells Reveals Viral and Host Etiologic Molecular Attributes of Autoimmunity in COVID-19.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Feb 22:2021.02.21.432171. doi: 10.1101/2021.02.21.432171. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: J Autoimmun. 2021 Jun;120:102644. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102644. PMID: 33655248 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
An Autoantigen Atlas From Human Lung HFL1 Cells Offers Clues to Neurological and Diverse Autoimmune Manifestations of COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 24;13:831849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.831849. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35401574 Free PMC article.
-
A master autoantigen-ome links alternative splicing, female predilection, and COVID-19 to autoimmune diseases.J Transl Autoimmun. 2022;5:100147. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2022.100147. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Transl Autoimmun. 2022. PMID: 35237749 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

