Integrating miRNA and mRNA Profiling to Assess the Potential miRNA-mRNA Modules Linked With Testicular Immune Homeostasis in Sheep
- PMID: 34113669
- PMCID: PMC8185144
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2021.647153
Integrating miRNA and mRNA Profiling to Assess the Potential miRNA-mRNA Modules Linked With Testicular Immune Homeostasis in Sheep
Abstract
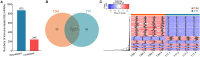
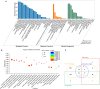
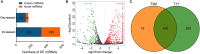
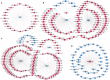
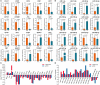
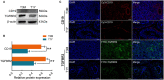
Beyond its well-known role in spermatogenesis and androgen production, mammalian testes are increasingly recognized as an immune-privileged organ for protecting autoantigenic germ cells, especially meiotic and postmeiotic germ cells, from systemic immune responses. Despite its importance, the molecular mechanisms underlying this regulation in mammals, including sheep, are far from known. In this study, we searched for the genes associated with testicular immune privilege and assessed their possible modulating mechanisms by analyzing systematic profiling of mRNAs and miRNAs on testicular tissues derived from prepubertal and postpubertal Tibetan sheep acquired by RNA sequencing. We identified 1,118 differentially expressed (DE) mRNAs associated with immunity (245 increased mRNAs and 873 decreased mRNAs) and 715 DE miRNAs (561 increased miRNAs and 154 decreased miRNAs) in postpubertal testes compared with prepuberty. qPCR validations for 20 DE mRNAs and 16 miRNAs showed that the RNA-seq results are reliable. By using Western blot, the postpubertal testes exhibited decreased protein abundance of CD19 and TGFBR2 (two proteins encoded by DE mRNAs) when compared with prepuberty, consistent with mRNA levels. The subsequent immunofluorescent staining showed that the positive signals for the CD19 protein were observed mainly in Sertoli cells and the basement membrane of pre- and postpubertal testes, as well as the prepubertal testicular vascular endothelium. The TGFBR2 protein was found mostly in interstitial cells and germ cells of pre- and postpubertal testes. Functional enrichment analysis indicated that DE mRNAs were mainly enriched in biological processes or pathways strongly associated with the blood-testis barrier (BTB) function. Many decreased mRNAs with low expression abundance were significantly enriched in pathways related to immune response. Also, multiple key miRNA-target negative correlation regulatory networks were subsequently established. Furthermore, we verified the target associations between either oar-miR-29b or oar-miR-1185-3p and ITGB1 by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Finally, a putative schematic model of the miRNA-mRNA-pathway network mediated by immune homeostasis-related genes was proposed to show their potential regulatory roles in sheep testicular privilege. Taken together, we conclude that many immune-related genes identified in this study are negatively regulated by potential miRNAs to participate in the homeostatic regulation of testicular immune privilege of sheep by sustaining BTB function and inhibiting immune responses under normal physiological conditions. This work offers the first global view of the expression profiles of miRNAs/mRNAs involved in sheep testicular immune privilege and how the genes potentially contribute to immune-homeostatic maintenance.
Keywords: RNA-seq; Tibetan sheep; blood-testis barrier; immune privilege; miRNA; testis.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Wang, Luo, An, Zhang, Zhao and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrated Analysis of miRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles Reveals Functional miRNA-Targets in Development Testes of Small Tail Han Sheep.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Feb 7;9(2):523-533. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200947. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30559255 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling Stage-Dependent Expression Patterns of Circular RNAs and Their Related ceRNA Modulation in Ovine Postnatal Testis Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 19;9:627439. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.627439. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33816472 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment, maintenance and functional integrity of the blood-testis barrier in organotypic cultures of fresh and frozen/thawed prepubertal mouse testes.Mol Hum Reprod. 2017 May 1;23(5):304-320. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gax017. Mol Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28333312
-
T Lymphocytes and Testicular Immunity: A New Insight into Immune Regulation in Testes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 23;22(1):57. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010057. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33374605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatic-Immune Cells Crosstalk In-The-Making of Testicular Immune Privilege.Reprod Sci. 2022 Oct;29(10):2707-2718. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00721-0. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Reprod Sci. 2022. PMID: 34580844 Review.
Cited by
-
Semen Quality, Testicular Cell Apoptosis, and Transcriptome Analysis Following Mild Scrotal Heat Stress in Wugu-Hu Crossbred and Hu Rams.Animals (Basel). 2025 Mar 3;15(5):724. doi: 10.3390/ani15050724. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40076007 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA and circular RNA profiling in the deposited fat tissue of Sunite sheep.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 4;9:954882. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.954882. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36406061 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Functional Assignment of Genes Implicated in Sperm Maturation of Tibetan Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2023 May 6;13(9):1553. doi: 10.3390/ani13091553. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37174590 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel-m0230-3p miRNA Modulates the CSF1/CSF1R/Ras Pathway to Regulate the Cell Tight Junctions and Blood-Testis Barrier in Yak.Cells. 2024 Aug 5;13(15):1304. doi: 10.3390/cells13151304. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120333 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome sequencing reveals differences between leydig cells and sertoli cells of yak.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Aug 24;9:960250. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.960250. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36090173 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

