Nasal Extracts from Patients with Alzheimer's Disease Induce Tau Aggregates in a Cellular Model of Tau Propagation
- PMID: 34113783
- PMCID: PMC8150252
- DOI: 10.3233/ADR-210298
Nasal Extracts from Patients with Alzheimer's Disease Induce Tau Aggregates in a Cellular Model of Tau Propagation
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence indicates that the misfolded tau protein can propagate aggregates between cells in a prion-like manner. This prion activity has been typically studied in brain extracts of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), but not in the olfactory region that can be a potential biomarker in AD.
Objective: To investigate the prion seeding activity of tau in nasal mucosa tissues using a cell culture model of tau propagation.
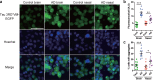
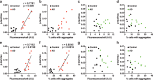
Methods: Brain and nasal mucosa homogenates were added to HEK293T cells expressing three repeat or four-repeat domains of tau with the L266V, V337M (3RD*VM) and P301L and V377M mutations (4RD*LM) fused to the enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP) respectively. We also measured the level of phosphorylated tau (p-tau), total tau (t-tau), and p-tau/t-tau ratio and performed correlation analysis between tau prion activity and the level of tau.
Results: We found that brain and nasal tissue homogenates from patients with AD significantly induced tau aggregation in HEK293T cells either expressing tau 3RD*VM-EGFP or 4RD*LM-EGFP compared with control brain and nasal tissue homogenates. The levels of p-tau and p-tau/t-tau ratio were significantly increased in the brain of patients with AD; however, no significant difference was found in nasal tissue compared with their respective control tissue homogenates.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the nasal tissues contain tau seeds, similar to the brain, albeit without changes in the levels of p-tau and t-tau. Therefore, a cellular bioassay using nasal tissues would have great potential as an AD biomarker because of the usefulness of nasal tissue biopsy.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; nasal extracts; tau aggregation; tau propagation.
© 2021 – The authors. Published by IOS Press.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was supported by Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Collinge J, Sidle KCL, Meads J, Ironside J, Hill AF (1996) Molecular analysis of prion strain variation and the aetiology of “new variant” CJD. Nature 383, 685–690. - PubMed
-
- Caughey B, Raymond GJ (1991) The scrapie-associated form of PrP is made from a cell surface precursor that is both protease- and phospholipase-sensitive. J Biol Chem 266, 18217–18223. - PubMed
-
- Castilla J, Saá P, Hetz C, Soto C (2005) In vitro generation of infectious scrapie prions. Cell 121, 195–206. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

