The mechanism of full activation of tumor suppressor PTEN at the phosphoinositide-enriched membrane
- PMID: 34113810
- PMCID: PMC8169795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102438
The mechanism of full activation of tumor suppressor PTEN at the phosphoinositide-enriched membrane
Abstract
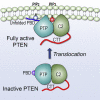
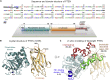
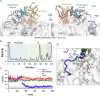
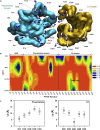
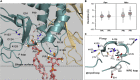
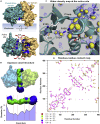
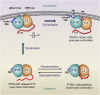
Tumor suppressor PTEN, the second most highly mutated protein in cancer, dephosphorylates signaling lipid PIP3 produced by PI3Ks. Excess PIP3 promotes cell proliferation. The mechanism at the membrane of this pivotal phosphatase is unknown hindering drug discovery. Exploiting explicit solvent simulations, we tracked full-length PTEN trafficking from the cytosol to the membrane. We observed its interaction with membranes composed of zwitterionic phosphatidylcholine, anionic phosphatidylserine, and phosphoinositides, including signaling lipids PIP2 and PIP3. We tracked its moving away from the zwitterionic and getting absorbed onto anionic membrane that harbors PIP3. We followed it localizing on microdomains enriched in signaling lipids, as PI3K does, and observed PIP3 allosterically unfolding the N-terminal PIP2 binding domain, positioning it favorably for the polybasic motif interaction with PIP2. Finally, we determined PTEN catalytic action at the membrane, all in line with experimental observations, deciphering the mechanisms of how PTEN anchors to the membrane and restrains cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; In Silico Biology; Structural Biology.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PTEN Dual Lipid- and Protein-Phosphatase Function in Tumor Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 28;14(15):3666. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153666. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding of the PH and polybasic C-terminal domains of ARNO to phosphoinositides and to acidic lipids.Biochemistry. 2000 May 16;39(19):5893-901. doi: 10.1021/bi992795w. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10801341
-
Regulation of PTEN function as a PIP3 gatekeeper through membrane interaction.Cell Cycle. 2006 Jul;5(14):1523-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.14.3005. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16861931 Review.
-
Engineering ePTEN, an enhanced PTEN with increased tumor suppressor activities.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 1;111(26):E2684-93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409433111. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24979808 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN inhibits BMI1 function independently of its phosphatase activity.Mol Cancer. 2009 Nov 10;8:98. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-98. Mol Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19903340 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulatory mechanisms triggered by enzyme interactions with lipid membrane surfaces.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 30;10:1306483. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1306483. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38099197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of FLOT1-related gene signature in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: insights into radioresistance mechanisms and clinical outcomes.Cell Death Discov. 2025 May 7;11(1):224. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02500-1. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40335491 Free PMC article.
-
Ras, RhoA, and vascular pharmacology in neurodevelopment and aging.Neurochem Int. 2024 Dec;181:105883. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105883. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Neurochem Int. 2024. PMID: 39427854 Review.
-
The allosteric mechanism of mTOR activation can inform bitopic inhibitor optimization.Chem Sci. 2023 Dec 7;15(3):1003-1017. doi: 10.1039/d3sc04690g. eCollection 2024 Jan 17. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38239681 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ferroptosis by PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: a promising therapeutic axis in cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Mar 18;12:1372330. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1372330. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38562143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

