A SMAD4-modulated gene profile predicts disease-free survival in stage II and III colorectal cancer
- PMID: 34114372
- PMCID: PMC8789617
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.1423
A SMAD4-modulated gene profile predicts disease-free survival in stage II and III colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer-related mortality in the United States and a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Loss of SMAD4, a critical tumor suppressor and the central node of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily, is associated with worse outcomes for colorectal cancer patients; however, it is unknown whether an RNA-based profile associated with SMAD4 expression could be used to better identify high-risk colorectal cancer patients.
Aim: Identify a gene expression-based SMAD4-modulated profile and test its association with patient outcome.
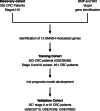
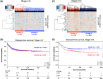
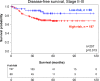
Methods and results: Using a discovery dataset of 250 colorectal cancer patients, we analyzed expression of BMP/Wnt target genes for association with SMAD4 expression. Promoters of the BMP/Wnt genes were interrogated for SMAD-binding elements. Fifteen genes were implicated and three tested for modulation by SMAD4 in patient-derived colorectal cancer tumoroids. Expression of the 15 genes was used for unsupervised hierarchical clustering of a training dataset and two resulting clusters modeled in a centroid model. This model was applied to an independent validation dataset of stage II and III patients. Disease-free survival was analyzed by the Kaplan-Meier method. In vitro analysis of three genes identified in the SMAD4-modulated profile (JAG1, TCF7, and MYC) revealed modulation by SMAD4 consistent with the trend observed in the profile. In the training dataset (n = 553), the profile was not associated with outcome. However, among stage II and III patients (n = 461), distinct clusters were identified by unsupervised hierarchical clustering that were associated with disease-free survival (p = .02, log-rank test). The main model was applied to a validation dataset of stage II/III CRC patients (n = 257) which confirmed the association of clustering with disease-free survival (p = .013, log-rank test).
Conclusions: A SMAD4-modulated gene expression profile identified high-risk stage II and III colorectal cancer patients, can predict disease-free survival, and has prognostic potential for stage II and III colorectal cancer patients.
Keywords: SMAD4; cancer biology; colorectal cancer; gene expression profile; tumor suppressor genes.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Joshua Smith has received travel support for fellow education (2015) from Intuitive Surgical Inc. J. Joshua Smith also served as clinical advisor (2019) for Guardant Health, Inc. Julio Garcia‐Aguilar has received support from Medtronic (honorarium for consultancy with Medtronic), Johnson & Johnson (honorarium for delivering a talk), and Intuitive Surgical (honorarium for participating in a webinar by Intuitive Surgical Inc.). All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- UpToDate . Observed survival rates for 28,491 cases with adenocarcinoma of the colon. 2010.
-
- Benson AB 3rd, Venook AP, Cederquist L, et al. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: colon cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2017;15:370‐398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Colorectal Cancer Alliance
- 5R01-CA182551-04/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Chris4Life Research Award
- P30 CA008748/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA182551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Colorectal Cancer Research Center
- P50 CA095103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA069457/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- John Wasserman Colon and Rectal Cancer Fund
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA069457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA158472/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA240139/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA248289/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

