Systematic review: societal cost of illness of inflammatory bowel disease is increasing due to biologics and varies between continents
- PMID: 34114667
- PMCID: PMC8361769
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.16445
Systematic review: societal cost of illness of inflammatory bowel disease is increasing due to biologics and varies between continents
Abstract
Background: Knowledge of the cost of illness of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is essential for health policy makers worldwide.
Aim: To assess the cost of illness of IBD from the societal perspective taking into account time trends and geographical differences.
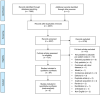
Methods: A systematic review of all population-based studies on cost of illness of IBD published in Embase, Medline, Web of Science and Google Scholar. Methodology of included studies was assessed and costs were adjusted to 2018 US dollars.
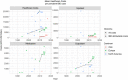
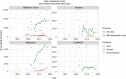
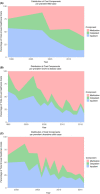
Results: Study methodologies differed considerably, with large differences in perspective, valuation method and population. For prevalent Crohn's disease (CD) cases in the last ten years annual healthcare costs were in Asia $4417 (range $1230-$31 161); Europe $12 439 ($7694-$15 807) and North America $17 495 ($14 454-$20 535). For ulcerative colitis (UC), these were $1606 ($309-$14 572), $7224 ($3228-$9779) and $13 559 ($13 559-$13 559). The main cost driver was medication, the cost of which increased considerably between 1985 and 2018, while outpatient and inpatient costs remained stable. IBD had a negative impact on work productivity. Annual costs of absenteeism for CD and UC were in Asia (with presenteeism) $5638 ($5638-$5638) and $4828 ($4828-$4828); Europe $2660 ($641-$5277) and $2394 ($651-$5992); North America $752 ($307-$1303) and $1443 ($85-$2350).
Conclusion: IBD societal cost of illness is increasing, driven by growing costs of medication, and varies considerably between continents. While biologic therapy was expected to decrease inpatient costs by reducing hospitalisations and surgery, these costs have not declined.
© 2021 The Authors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:711–721. - PubMed
-
- Sands BE, Sandborn WJ, Panaccione R, et al. Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1201–1214. - PubMed
-
- Colombel J, Sandborn WJ, Rutgeerts P, et al. Adalimumab for maintenance of clinical response and remission in patients with Crohn's disease: the CHARM trial. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:52–65. - PubMed
-
- Sandborn WJ, Su C, Sands BE, et al. Tofacitinib as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1723–1736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
