Attentional Modulation of Hierarchical Speech Representations in a Multitalker Environment
- PMID: 34115102
- PMCID: PMC8491717
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhab136
Attentional Modulation of Hierarchical Speech Representations in a Multitalker Environment
Abstract
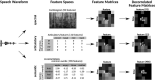
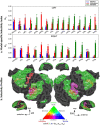
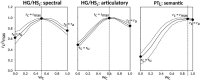
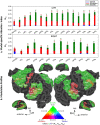
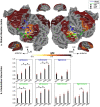
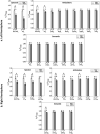
Humans are remarkably adept in listening to a desired speaker in a crowded environment, while filtering out nontarget speakers in the background. Attention is key to solving this difficult cocktail-party task, yet a detailed characterization of attentional effects on speech representations is lacking. It remains unclear across what levels of speech features and how much attentional modulation occurs in each brain area during the cocktail-party task. To address these questions, we recorded whole-brain blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) responses while subjects either passively listened to single-speaker stories, or selectively attended to a male or a female speaker in temporally overlaid stories in separate experiments. Spectral, articulatory, and semantic models of the natural stories were constructed. Intrinsic selectivity profiles were identified via voxelwise models fit to passive listening responses. Attentional modulations were then quantified based on model predictions for attended and unattended stories in the cocktail-party task. We find that attention causes broad modulations at multiple levels of speech representations while growing stronger toward later stages of processing, and that unattended speech is represented up to the semantic level in parabelt auditory cortex. These results provide insights on attentional mechanisms that underlie the ability to selectively listen to a desired speaker in noisy multispeaker environments.
Keywords: cocktail-party; dorsal and ventral stream; encoding model; fMRI; natural speech.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permission@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Alho K, Medvedev SV, Pakhomov SV, Roudas MS, Tervaniemi M, Reinikainen K, Zeffirio T, Näätänen R. 1999. Selective tuning of the left and right auditory cortices during spatially directed attention. Cogn Brain Res. 7:335–341. - PubMed
-
- Alho K, Vorobyev VA, Medvedev SV, Pakhomov SV, Roudas MS, Tervaniemi M, Näätänen R. 2003. Hemispheric lateralization of cerebral blood-flow changes during selective listening to dichotically presented continuous speech. Cogn Brain Res. 17:201–211. - PubMed
-
- Alho K, Vorobyev VA, Medvedev SV, Pakhomov SV, Starchenko MG, Tervaniemi M, Näätänen R. 2006. Selective attention to human voice enhances brain activity bilaterally in the superior temporal sulcus. Brain Res. 1075:142–150. - PubMed
-
- Alho K, Rinne T, Herron TJ, Woods DL. 2014. Stimulus-dependent activations and attention-related modulations in the auditory cortex: a meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Hear Res. 307:29–41. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Statist Soc. 57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

