US Population-referenced Percentiles for Wrist-Worn Accelerometer-derived Activity
- PMID: 34115727
- PMCID: PMC8516690
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002726
US Population-referenced Percentiles for Wrist-Worn Accelerometer-derived Activity
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to present age- and sex-specific percentiles for daily wrist-worn movement metrics in US youth and adults. This metric represents a summary of all recorded movement, regardless of the purpose, context, or intensity.
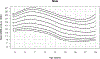
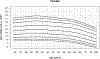
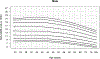
Methods: Wrist-worn accelerometer data from the combined 2011-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey cycles and the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey National Youth Fitness Survey were used for this analysis. Monitor-Independent Movement Summary units (MIMS-units) from raw triaxial accelerometer data were used. We removed the partial first and last assessment days and days with ≥5% nonwear time. Participants with ≥1 valid day were included. Mean MIMS-units were calculated across all valid days. Percentile tables and smoothed curves of daily MIMS-units were calculated for each age and sex using the Generalized Additive Models for Location Shape and Scale.
Results: The analytical sample included 14,705 participants age ≥3 yr. The MIMS-unit activity among youth was similar for both sexes, whereas adult females generally had higher MIMS-unit activity than did males. Median daily MIMS-units peaked at age 6 yr for both sexes (males, 20,613; females, 20,706). Lowest activity was observed for males and females 80+ yr of age: 8799 and 9503, respectively.
Conclusions: Population referenced MIMS-unit percentiles for US youth and adults are a novel means of characterizing total activity volume. By using MIMS-units, we provide a standardized reference that can be applied across various wrist-worn accelerometer devices. Further work is needed to link these metrics to activity intensity categories and health outcomes.
Copyright © 2021 by the American College of Sports Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests, including financial interests or affiliations. The National Institutes of Health reviewed and approved this article before submission. The results of this study are presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation. The results of the present study do not constitute endorsement by the American College of Sports Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Bassett DR, Troiano RP, McClain JJ, Wolff DL. Accelerometer-based physical activity: total volume per day and standardized measures. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(4):833–8. - PubMed

