Modulatory Potential of Cannabidiol on the Opioid-Induced Inflammatory Response
- PMID: 34115948
- PMCID: PMC8217599
- DOI: 10.1089/can.2020.0181
Modulatory Potential of Cannabidiol on the Opioid-Induced Inflammatory Response
Abstract
Opioids are effective analgesics; however, there are many negative consequences of chronic use. One important side effect of chronic opioid use is the continuous engagement of the immune response that can exacerbate chronic pain. The opioid, morphine, initiates a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling cascade that drives the activation of NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome proteins, resulting in cytokine production and effectively creating a positive feedback loop for continuous TLR4 activation. In addition to driving cytokine production, morphine drives changes in proinflammatory lipid signaling. The alteration of both cytokine and lipid signaling systems by morphine suggests that its chronic use leads to a pathological immune response that would benefit from targeted therapy. Engaging the endogenous cannabinoid system has shown therapeutic benefit, particularly regarding its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. Promising preclinical and clinical investigations suggest that cannabidiol (CBD) is an effective adjuvant for treatment of symptoms of opioid use disorders; however, the mechanism through which CBD drives this outcome is unclear. One potential source of insight into this mechanism is in how CBD regulates immune regulators such as cytokines and lipid signaling systems, including endocannabinoids and related immune-responsive lipids. In this review, we outline the immune response to chronic opioid use as well as CBD in the context of a lipopolysaccharide-induced immune response and speculate on the mechanism of CBD as a modulator of chronic opioid-induced immune system dysregulation.
Keywords: LPS; TLR4; cannabidiol; cytokines; inflammation; morphine.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
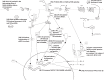

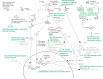
References
-
- Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:805–820 - PubMed
-
- Paudel YN, Angelopoulou E, Piperi C, et al. . Shaikh, Enlightening the role of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in inflammation: updates on receptor signalling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;858:172487. - PubMed
-
- Luo L, Lucas RM, Liu L, et al. . Signalling, sorting and scaffolding adaptors for Toll-like receptors. J Cell Sci. 2019;133:cs239194 - PubMed
-
- Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J. The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell. 2002;10:417–426 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

