The methamphetamine epidemic among persons who inject heroin in Hai Phong, Vietnam
- PMID: 34116818
- PMCID: PMC8197775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsat.2021.108320
The methamphetamine epidemic among persons who inject heroin in Hai Phong, Vietnam
Abstract
Aims: To describe the current methamphetamine (MA) use epidemic among persons who inject heroin (PWID) in Hai Phong, Vietnam, and consider possibilities for mitigating adverse effects of methamphetamine use.
Methods: This study conducted surveys of PWID in 2016, 2017, and 2018 (N = 1383, 1451, and 1445, respectively). Trained interviewers administered structured interviews covering drug use histories, current drug use, and related risk behaviors. The study used urinalysis to confirm current drug use, and conducted HIV and HCV testing.
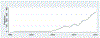
Results: Participants were predominantly male (95%), mean age of 40, and all reported injecting heroin. Respondents' reports of initiating MA use were rare up through early 2000s but increased exponentially through the mid-2010s. MA use was predominantly "smoking," heating the drug and inhaling the vapor using a pipe; injecting MA was rare. Current (past 30 day) MA use appears to have plateaued in 2016-2018 with 53-58% of participants reporting no use in the last 30 days, 37-41% reporting low to moderate use (1 to 19 days in last 30 days), and 5-7% reporting very frequent use (20 or more days in last 30 days). This plateau reflects a rough balance between new users and individuals ceasing use.
Conclusions: MA use has become a substantial public health problem among PWID in Hai Phong. Initiation into MA use rose exponentially from 2005 to about 2015. Use of MA will likely continue for a substantial number of PWID. Currently, no medication is approved for treating MA disorders in Vietnam. Current psychosocial treatment requires highly trained counselors and months of treatment, so that psychosocial treatment for all PWID with MA disorders is likely beyond the resources available in a middle-income country such as Vietnam. Harm reduction programs implemented by community-based organization staff may provide a way to rapidly address aspects of the current MA epidemic. Such programs could emphasize social support for reducing use where possible and for avoiding escalation of use among persons continuing to use.
Keywords: Hai Phong; Heroin; Mental health; Methamphetamine; Persons who inject drugs; Viet Nam; Vietnam.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest declaration: none
Figures
References
-
- Beyrer C, Razak MH, Lisam K, Chen J, Lui W, & Yu X-F (2000). Overland heroin trafficking routes and HIV-1 spread in south and south-east Asia. AIDS, 14(1), 75–83. - PubMed
-
- Des Jarlais DC, Khue PM, Feelemyer J, Arasteh K, Thi Huong D, Thi Hai Oanh K, … Nagot N (2019). Combined Prevention + Large Community Surveys = End of the HIV Epidemic among PWID in Hai Phong, Vietnam. Paper presented at the International AIDS Society Malaysia, Malaysia.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous