Autoimmune Disease and Breast Implants: Systematic Review of Outcomes
- PMID: 34117137
- PMCID: PMC8660949
- DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002930
Autoimmune Disease and Breast Implants: Systematic Review of Outcomes
Abstract
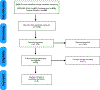
Given that the use of breast implants for both cosmetic and reconstructive purposes is growing in the United States, an evaluation of factors that may affect the outcome of breast implant surgery is needed. A systematic review was conducted to evaluate the question: Does a personal or family history of autoimmune disease affect outcomes in breast implant surgery? The literature search yielded 2425 records, but after removal of duplicates, abstract screening, and full-text assessment, only 2 studies met the inclusion criteria for the final review. Both studies provided level III evidence and the average Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies score was 16.5 (range, 15-18 of 24), indicating a fair level of evidence overall. This systematic review found no evidence to support that a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease and/or a family history of autoimmune diseases will lead to poor surgical outcomes in breast implant surgery. Further study is warranted.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none declared.
Figures
References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons (2019) Plastic surgery statistics report. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2019/plastic-su.... Accessed 5 October 2020
-
- NIH Autoimmune Diseases Coordinating Committee (March 2005) Progress in autoimmune diseases research. https://www.niaid.nih.gov/sites/default/files/adccfinal.pdf. Accessed 5 October 2020
-
- Goodnow CC (2007) Multistep pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Cell 130 (1):25–35 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous