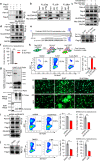
Palmitoylation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein is essential for viral infectivity
- PMID: 34117209
- PMCID: PMC8193602
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00651-y
Palmitoylation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein is essential for viral infectivity
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment on
-
Palmitoylation of NOD1 and NOD2 is required for bacterial sensing.Science. 2019 Oct 25;366(6464):460-467. doi: 10.1126/science.aau6391. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Science. 2019. PMID: 31649195
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

