A modified transconjunctival technique for botulinum toxin chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris for corneal protection
- PMID: 34117397
- PMCID: PMC9151670
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-021-01587-x
A modified transconjunctival technique for botulinum toxin chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris for corneal protection
Abstract
Background: Botulinum toxin (BTX) is useful for inducing temporary ptosis in patients with ocular surface disease. However, transcutaneous BTX often causes inadvertent superior rectus (SR) paresis. Furthermore, Muller's muscle is unaffected by transcutaneous BTX, resulting in lagophthalmos and incomplete ptosis.
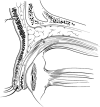
Methods: We report a novel BTX injection technique, in which the upper lid is double everted over a Desmarres retractor, and BTX injected transconjunctivally at the superior aspect of Muller's muscle, where it lies close to levator palpebrae superioris.
Results: In our series of 21 patients, one had inadvertent subcutaneous BTX and developed incomplete ptosis. The remaining 20 patients had complete ptosis within 48 h. No patients had SR underaction.
Conclusion: We conclude that transconjunctival BTX injection is safe, effective, and superior to transcutaneous BTX injection, because of the low risk of superior rectus underaction and incomplete ptosis.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to The Royal College of Ophthalmologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

