Closed but Not Protected: Excess Deaths Among the Amish and Mennonites During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 34117598
- PMCID: PMC8195242
- DOI: 10.1007/s10943-021-01307-5
Closed but Not Protected: Excess Deaths Among the Amish and Mennonites During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Closed but Not Protected: Excess Deaths Among the Amish and Mennonites During the COVID‑19 Pandemic.J Relig Health. 2022 Apr;61(2):1766. doi: 10.1007/s10943-022-01530-8. J Relig Health. 2022. PMID: 35175507 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Correction to: Closed but Not Protected: Excess Deaths Among the Amish and Mennonites During the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Relig Health. 2024 Oct;63(5):4047-4048. doi: 10.1007/s10943-024-02093-6. J Relig Health. 2024. PMID: 39096442 No abstract available.
Abstract
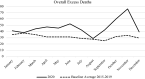
"Excess deaths" is a means to estimate the lethality of COVID-19 (directly and indirectly). Assessing "excess death" in closed religious communities provides information on how COVID-19 impacted these communities. We use obituary information published in an Amish/Mennonite newspaper to examine excess death among the Amish/Mennonites in 2020. Our results indicate the Amish/Mennonite excess death rates are similar to the national trends in the USA. The excess death rate for Amish/Mennonites spiked with a 125% increase in November 2020. The impact of COVID-19 on this closed religious community highlights the need to consider religion to stop the spread of COVID-19.
Keywords: Amish; COVID-19; Closed religious groups; Excess death.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
"The Graves Cannot Be Dug Fast Enough": Excess Deaths Among US Amish and Mennonites During the 1918 Flu Pandemic.J Relig Health. 2024 Feb;63(1):652-665. doi: 10.1007/s10943-023-01899-0. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Relig Health. 2024. PMID: 37656304
-
Pathways to Immunity: Patterns of Excess Death Across the United States and Within Closed Religious Communities.J Relig Health. 2023 Aug;62(4):2820-2835. doi: 10.1007/s10943-023-01838-z. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Relig Health. 2023. PMID: 37261578 Free PMC article.
-
Rituals of Contagion in Closed Religious Communities: A Case Study of Amish and Mennonite Communities in the USA During the Beginning of the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Relig Health. 2022 Oct;61(5):4260-4281. doi: 10.1007/s10943-022-01615-4. Epub 2022 Jul 26. J Relig Health. 2022. PMID: 35882764 Free PMC article.
-
"A Divine Infection": A Systematic Review on the Roles of Religious Communities During the Early Stage of COVID-19.J Relig Health. 2022 Feb;61(1):866-919. doi: 10.1007/s10943-021-01364-w. Epub 2021 Aug 17. J Relig Health. 2022. PMID: 34405313 Free PMC article.
-
Religion in the US during the time of a Pandemic: A Medical Perspective.J Relig Health. 2021 Oct;60(5):3177-3192. doi: 10.1007/s10943-021-01366-8. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Relig Health. 2021. PMID: 34338954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
"The Graves Cannot Be Dug Fast Enough": Excess Deaths Among US Amish and Mennonites During the 1918 Flu Pandemic.J Relig Health. 2024 Feb;63(1):652-665. doi: 10.1007/s10943-023-01899-0. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Relig Health. 2024. PMID: 37656304
-
Metapopulation dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in a small-scale Amazonian society.PLoS Biol. 2023 Aug 22;21(8):e3002108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002108. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37607188 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Religions in the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 17;20(3):1691. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031691. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathways to Immunity: Patterns of Excess Death Across the United States and Within Closed Religious Communities.J Relig Health. 2023 Aug;62(4):2820-2835. doi: 10.1007/s10943-023-01838-z. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Relig Health. 2023. PMID: 37261578 Free PMC article.
-
Rituals of Contagion in Closed Religious Communities: A Case Study of Amish and Mennonite Communities in the USA During the Beginning of the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Relig Health. 2022 Oct;61(5):4260-4281. doi: 10.1007/s10943-022-01615-4. Epub 2022 Jul 26. J Relig Health. 2022. PMID: 35882764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armer JM, Radina ME. Definition of health and health promotion behaviors among midwestern old order Amish families. Journal of Multicultural Nursing and Health. 2006;12(3):44–53.
-
- Bainbridge WS, Stark R. Sectarian tension. Review of Religious Research. 1980;22(2):105–124. doi: 10.2307/3510654. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical