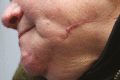
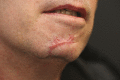
Facial Scars Due to Prone Position Pressure Ulcers: Underestimated Sequelae in COVID-19 Survivors?
- PMID: 34117861
- PMCID: PMC8344651
- DOI: 10.1093/asj/sjab251
Facial Scars Due to Prone Position Pressure Ulcers: Underestimated Sequelae in COVID-19 Survivors?
Figures
References
-
- Nazerali RS, Song KR, Wong MS. Facial pressure ulcer following prone positioning. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63(4):e413-e414. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical