IL-31, itch and hematological malignancies
- PMID: 34118946
- PMCID: PMC8199420
- DOI: 10.1186/s12948-021-00148-7
IL-31, itch and hematological malignancies
Abstract
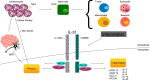
Pruritus is one of the most common symptoms experienced by neoplastic patients. The pathogenesis of neoplastic itch is complex and multifactorial and could be due to an unbalanced production of humoral mediators by altered immune effector cells. IL-31 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine produced by CD4 + T helper cells. The aim of this review was to evaluate the role of this Th2 cytokine and its receptor IL-31RA, in the onset of neoplastic pruritus. We analysed scientific literature looking for the most relevant original articles linking IL-31to itch in oncologic diseases. Interleukin-31 seems to be a main itch mediator in several hematologic disease such as Cutaneous T cells lymphomas. In these patients IL-31 was positively linked to itch level, and IL-31 matched with disease stage. IL-31 seems to play an important role in the signalling pathway involved in pruritus, but it is also suggested to play a proinflammatory and immunomodulatory role which could play a part in the progression of the neoplastic disease. Further studies will be fundamental in facing pruritus in oncologic patients, since this problem compromise their quality of life worsening an already critic picture.
Keywords: Cancer; Cytokines; IL-31; IL-33; Itch; Malignancies; Pruritus; Skin.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the author have any conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Itch in dermatomyositis: the role of increased skin interleukin-31.Br J Dermatol. 2018 Sep;179(3):669-678. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16498. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Br J Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29494763 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma and Pruritus: The Expression of IL-31 and its Receptors in the Skin.Acta Derm Venereol. 2016 Nov 2;96(7):894-898. doi: 10.2340/00015555-2417. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016. PMID: 27001482
-
Interleukin-31 and Pruritic Skin.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 28;10(9):1906. doi: 10.3390/jcm10091906. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33924978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-31 is overexpressed in skin and serum in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas but does not correlate to pruritus.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2022 Feb;39(1):81-87. doi: 10.5114/ada.2020.100824. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2022. PMID: 35369626 Free PMC article.
-
Pruritus as a Distinctive Feature of Type 2 Inflammation.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Mar 23;9(3):303. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9030303. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807098 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic-Based Platelet Activation-Associated Protein SELP May Be a Novel Biomarker for Coagulation and Prognostic in Essential Thrombocythemia.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 30;12(3):1078. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031078. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769725 Free PMC article.
-
The Anti-Cancer Effect of Cinnamon Aqueous Extract: A Focus on Hematological Malignancies.Life (Basel). 2023 May 12;13(5):1176. doi: 10.3390/life13051176. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37240821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Canine interleukin-31 binds directly to OSMRβ with higher binding affinity than to IL-31RA.3 Biotech. 2023 Sep;13(9):302. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03724-7. Epub 2023 Aug 14. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37588794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bilsborough J, Leung DYM, Maurer M, Howell M, Boguniewcz M, Yao L, Storey H, LeCiel C, Harder B, Gross JA. IL-31 is associated with cutaneous lymphocyte antigen–positive skin homing T cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:418–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.10.046. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials